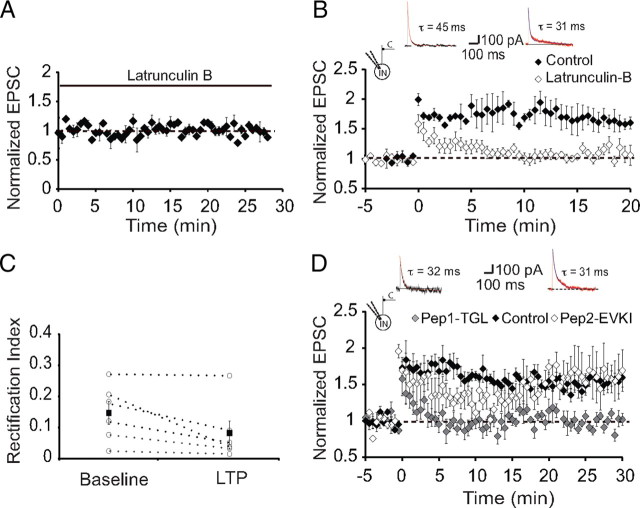
Figure 7.
LTP requires a functional actin cytoskeleton and SAP97. A, Lactrunculin B had no effect on basal synaptic transmission. Shown are average data of recordings from neurons with fast NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents in interneurons loaded with latrunculin B (20 μm; n = 4). B, Loading neurons with latrunculin B blocks LTP. Average data of recordings from neurons with fast NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents in interneurons loaded with latrunculin B (20 μm; n = 4; open diamonds). For comparison, interleaved recordings from neurons that were not loaded with latrunculin B (n = 4; filled diamonds). Inset, Representative NMDAR-mediated EPSCs in control and latrunculin-loaded neurons. C, AMPA receptors inserted after LTP lack GluR2 subunits. Shown is the RI of AMPA receptor EPSCs recorded before and after induction of LTP. Average RI is not significantly changed after tetanic stimulation, showing that receptors inserted after LTP also lack GluR2 subunits. D, LTP in interneurons requires interaction of GluR1 with its PDZ binding partners. Average data of recordings from neurons with fast NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents in interneurons loaded with pep1-TGL (50 μm; n = 6; open squares). For comparison, interleaved recordings from neurons that were loaded with pep2-EVKI (n = 5; gray squares) and neurons that were not loaded with any peptide (filled squares; n = 4) are shown. Inset, Representative NMDAR-mediated EPSCs in pep2-EVKI- and pep1-TGL-loaded neurons.