Figure 7.
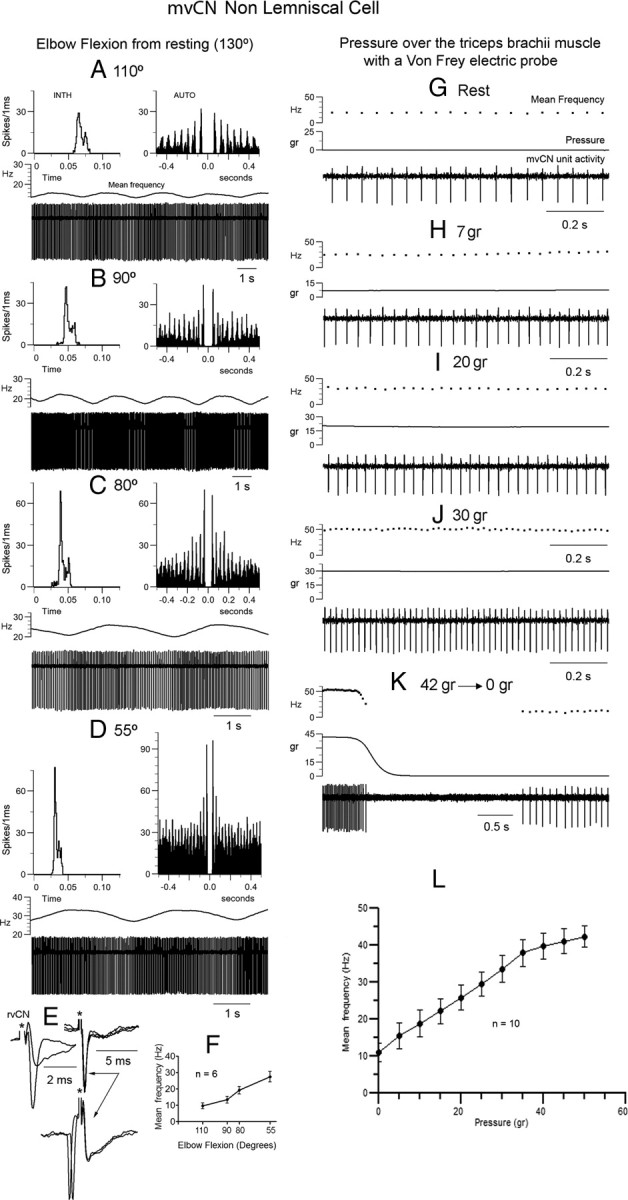
mvCN neurons were sensitive to muscle steady stretch. Same non-CL neuron. A–D, This non-CL cell showed a slow rhythmic activity at ∼0.4 Hz. The elbow joint was gradually flexed from rest (130°) and maintained at each new position for 5 min. The activity of the non-CL cell gradually incremented with lengthening of extensors. INTH, Interval interspike histogram; AUTO, autocorrelogram. E, This presumed interneuron responded antidromically to rvCN stimulation. The two superimpositions at left show the all or none nature of the antidromic spike and the superimposed records at right illustrate the collision test. F, Histogram (mean ± SEM) showing an almost linear increase in activity with elbow flexion for six different cells (4 CL). G–K, Increasing the steady pressure applied to the triceps brachii produced a similar increase in frequency as that observed with steady stretch. Note the firing silence at the end of stimulation (K). L, Histogram illustrating the mean ± SEM frequency increase with pressure for 10 different cells (7 CL).
