Figure 13.
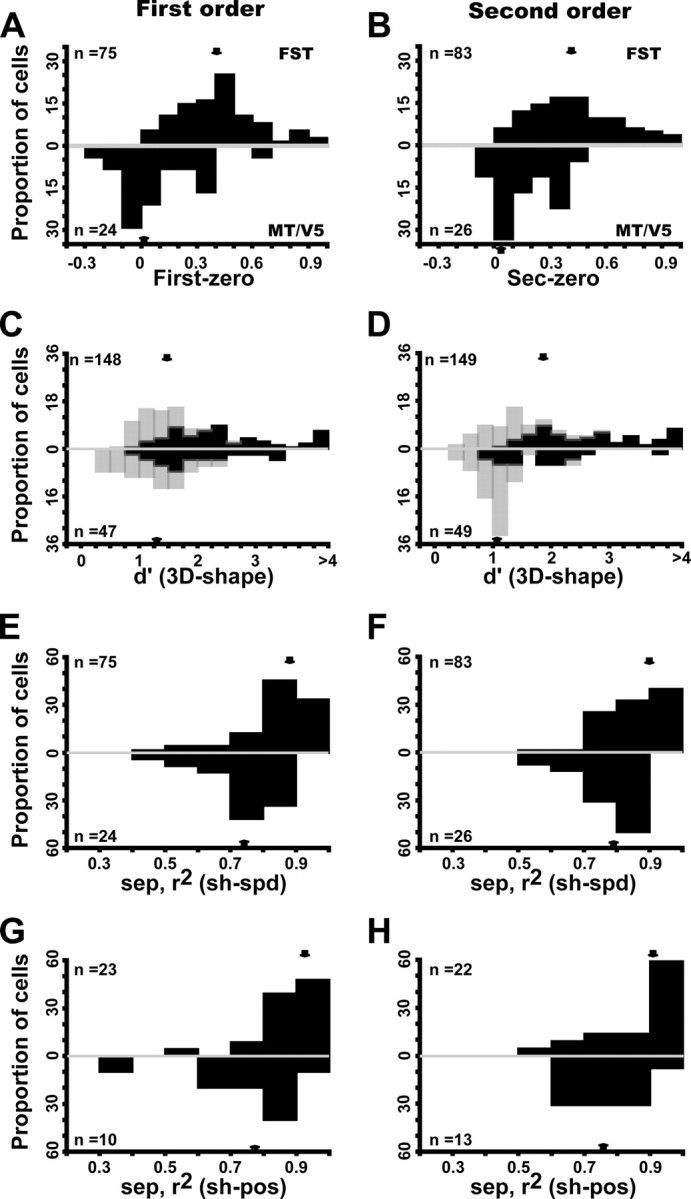
Comparison of MT/V5 (below) and FST (above) neurons tested with small stimuli and selective for first-order (A, C, E, G) and second-order (B, D, F, H) stimuli. A, B, Distribution of index [(Rnz − Rz)/(Rnz + Rz)], where Rnz and Rz are responses to nonzero and zero order, respectively; first-order FST median, 0.40 (0.28–0.56); MT/V5 median, 0.04 (−0.03 to 0.24). Distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 5.5, p < 10−6, Mann–Whitney U test); second-order FST median, 0.40 (0.26–0.58); MT/V5 median, 0.15 (−0.05 to 0.30). Distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 4.1, p < 10−3, Mann–Whitney U test). C, D, Distribution of d′ (for 3D shape): light and dark hatching indicate nonselective and selective according to ANOVA: first-order FST median, 1.66 (1.18–2.37); MT/V5 median, 1.47 (0.99–1.96); distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 2.16, p < 0.03, Mann–Whitney U test); second-order FST median, 1.8 (1.26–2.78); MT/V5 median, 1.12 (0.96–1.47). Distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 4.6, p < 10−5, Mann–Whitney U test). E, F, Distributions of 3D shape–speed separability index; first-order FST median, 0.88 (0.80–0.92); MT/V5 median, 0.75 (0.70–0.81); distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 4.47, p < 10−5, Mann–Whitney U test); second-order FST median, 0.86 (0.80–0.93); MT/V5 median, 0.79 (0.71–0.84); distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 3.88, p < 10−3, Mann–Whitney U test). G, H, Distributions of 3D shape–position separability index: first-order FST median, 0.92 (0.84–0.96); MT/V5 median, 0.79 (0.66–0.90); distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 2.48, p < 0.02, Mann–Whitney U test); second-order FST median, 0.92 (0.79–0.95); MT/V5 median, 0.76 (0.69–0.80); distribution significantly higher for FST (Z = 2.04, p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test). Arrows indicate median values.
