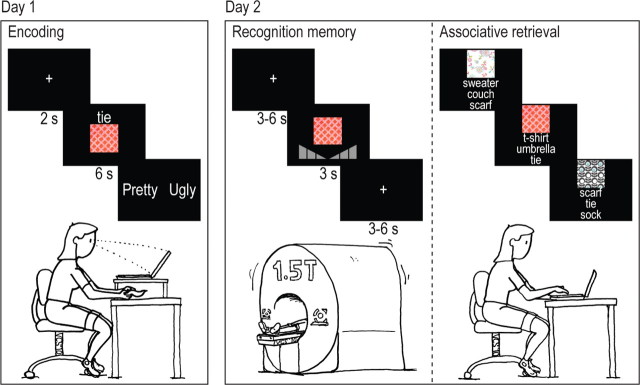
Figure 1.
Experimental design. On day 1, participants learned associations of visual motifs and congruent or incongruent object–fabric combinations, where the object was presented together with the motif as a written word on the computer screen, and the fabric simultaneously as a tactile stimulus underneath the computer screen. On day 2, participants were tested in the MR scanner by means of a visual item recognition test (motifs) and subsequently with an associative memory test outside the MR scanner in which the motifs served as cues and the associated word was asked for in a three-choice test.