Figure 5.
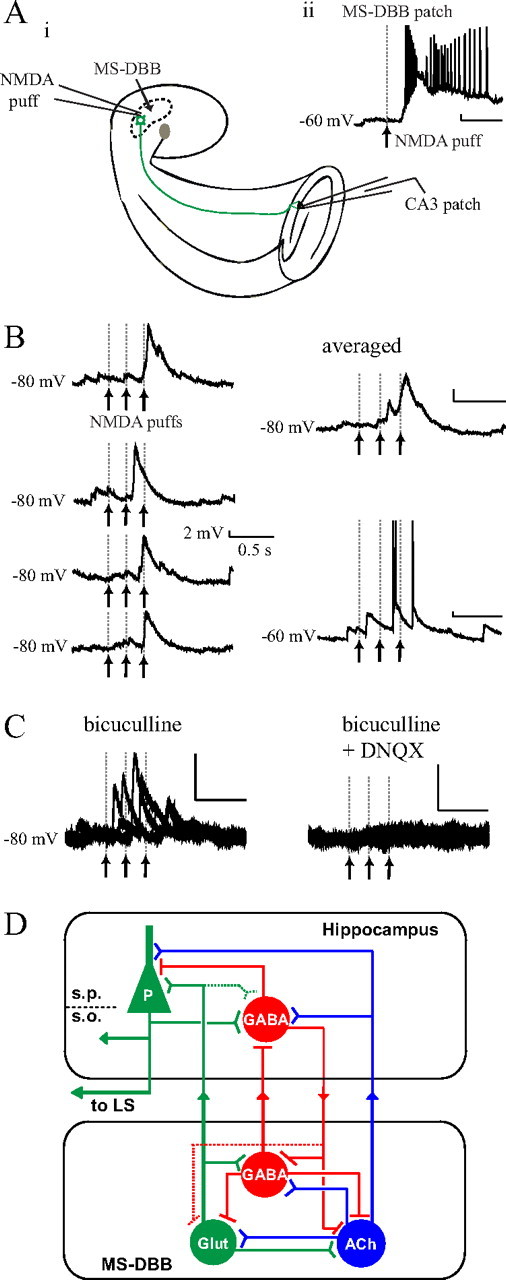
Local NMDA microinfusions to the MS-DBB triggered glutamatergic responses in CA3 pyramidal cells. Ai, In the septohippocampal preparation, MS-DBB neurons were locally activated by infusing small amounts of NMDA directly into the MS-DBB area using a puffer pipette while recording from CA3 pyramidal cells. Aii, A single NMDA application (200 μm, 100 ms) robustly depolarized a nearby VGLUT2-eGFP-(+) MS-DBB neuron. B, CA3 pyramidal cells responded to NMDA injections in the MS-DBB with EPSPs that were clearly time-locked to the stimuli (left: four consecutive trials at −80 mV; right top: averaged trace at −80 mV; right bottom: a raw trace at −60 mV). C, The EPSPs were abolished by 20 μm DNQX, indicating that the response was mediated by glutamate. D, A new model of the septohippocampal network: a subset of glutamatergic MS-DBB neurons may serve as intrinsic rhythm generators that can contribute a rhythmic excitatory drive to the local septal network as well as to the hippocampus. In the model, solid lines represent physiologically confirmed pathways and dotted lines indicate pathways that remain to be demonstrated. ACh, Acetylcholine; Glut, Glutamate; LS, lateral septum; S.P., stratum pyramidale; S.O., stratum oriens; P, pyramidal cell.
