Figure 5.
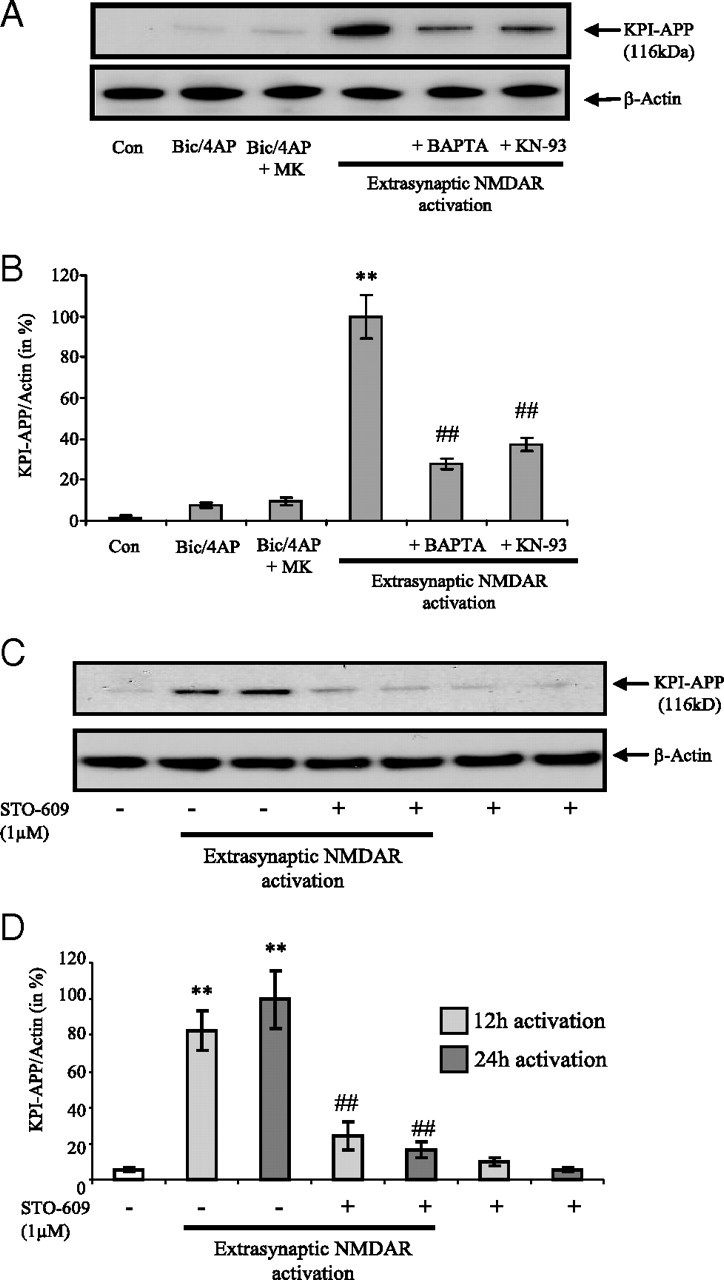
KPI-APP protein expression in cortical neurons exposed to extrasynaptic NMDAR activation is mediated by calcium signaling pathway. A, Immunoblotting analysis of KPI-APP protein in cortical neuron cultures 24 h after synaptic NMDAR activation with or without MK-801 blocking, or after extrasynaptic NMDAR activation (extrasynaptic protocol) in the presence or not of 10 μm BAPTA-AM, an intracellular calcium chelator, or 10 μm KN-93, an inhibitor of CaM kinases. Blots were rehybridized with an anti-actin antibody to estimate the total amount of proteins loaded. B, Relative expression of KPI-APP compared with actin from experiments presented in A. Densitometric analysis of the protein bands was performed with ImageJ software. Each column is the mean ± SD from three immunoblots (n = 3). Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 3; **p < 0.01 vs control; ##p < 0.01 vs extrasynaptic NMDAR activation). C, Immunoblotting analysis of KPI-APP protein in cortical neuron cultures 12 and 24 h after extrasynaptic NMDAR activation in the presence or not of 1 μm STO-609, a selective Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase. Blots were rehybridized with an anti-actin antibody to estimate the total amount of proteins loaded. D, Relative expression of KPI-APP compared with actin from experiments presented in C. Densitometric analysis of the protein bands was performed with ImageJ software. Each column is the mean ± SD from three immunoblots (n = 3). Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn's test (n = 3; **p < 0.01 vs respective control; ##p < 0.01 vs extrasynaptic NMDAR activation).
