Figure 6.
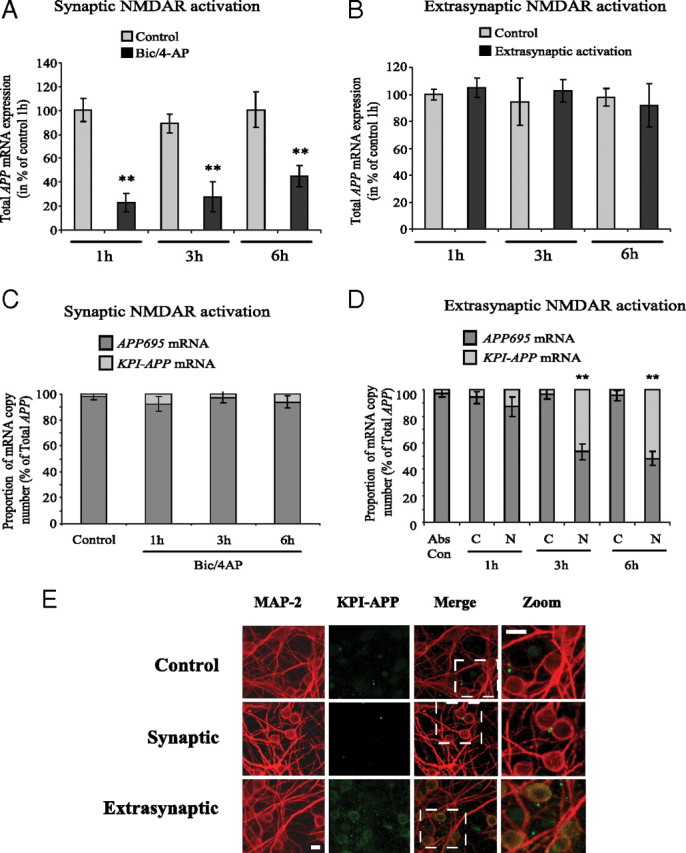
Synaptic NMDAR activation downregulates overall APP mRNA expression, whereas extrasynaptic NMDAR activation acts on APP isoforms mRNA ratio via an alternative splicing pathway. A, Real-time PCR analysis of total APP mRNA expression in cortical neurons exposed to Bic/4AP for 1, 3, or 6 h (synaptic protocol). A new pair of primers directed against the common part of the different APP isoforms was designed. At each time, APP mRNA expression in treated neurons was compared with its control. The expression level of APP was analyzed according to the ΔΔCt method (comparative Ct method) where Ct is the threshold cycle value and cyclophilin is the housekeeping gene. Results are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 9; **p < 0.01 to respective control). B, Real-time PCR analysis of total APP mRNA expression in cortical neurons exposed to extrasynaptic NMDAR activation for 1, 3, or 6 h (extrasynaptic protocol). At each time, APP mRNA expression in treated neurons was compared with its control. Results are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate and expression level of APP was analyzed according to the ΔΔCt method. C, APP695/KPI-APP mRNA ratio in cortical neuron cultures treated with 50 μm Bic/2.5 mm 4-AP for 1, 3, and 6 h (synaptic protocol). Absolute quantification of APP695 and KPI-APP mRNA in each sample was performed by real-time PCR using known concentrations of DNA standard molecules (PCR products). Histograms represent the relative part of the two mRNA populations with the total of both mRNA arbitrarily set at 100%. D, APP695/KPI-APP mRNA ratio in cortical neuron cultures exposed to 50 μm Bic/2.5 mm 4-AP for 2 min, and consecutively to Bic/4-AP with 10 μm MK801 for 3 min. After three extensive washings, cultures were incubated at 37°C for 1 h before the addition of 30 μm NMDA for 1, 3, and 6 h (extrasynaptic protocol). Absolute quantification of APP695 and KPI-APP mRNA in each sample was performed by real-time PCR using known concentrations of DNA standard molecules (PCR products) as described in Materials and Methods. Histograms represent the relative part of the two mRNA populations with the total of both mRNA arbitrarily set at 100%. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 3; **p < 0.01 vs respective control). Abs Con, Absolute control; C, control (Bic/4-AP and MK-801 blocking); N, NMDA treatment after MK-801 blocking. E, Expression of KPI-APP isoforms is induced in neurons exposed to extrasynaptic but not to synaptic NMDAR activation. Immunocytochemical analysis of KPI-APP expression in cultured cortical neurons subjected to synaptic or extrasynaptic NMDAR activation for 24 h. Neurons were stained with an antibody raised against the neuronal marker MAP-2 (red), and KPI-APP protein expression was determined by using the monoclonal antibody directed against the KPI domain of APP (green). KPI-APP appeared colocalized (yellow) to neuronal cytosol and plasma membrane when images were overlaid. No expression of KPI-APP was detected in neurons exposed to Bic/4-AP for 24 h (synaptic protocol). Scale bars, 20 μm.
