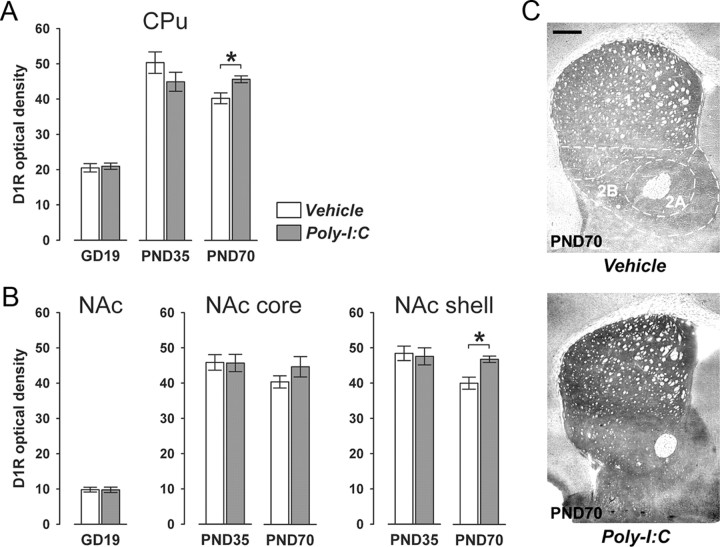
Figure 5.
Postpubertal onset of altered D1R expression in striatal regions following prenatal immune challenge. Pregnant mice were exposed to the viral mimic Poly-I:C or vehicle treatment, and the effects on striatal D1R expression were studied in the resulting offspring at the fetal (GD19), peripubertal (PND35), and adult (PND70) stages of development using optical densitometry of immunohistochemically stained coronal brain sections. A, Offspring born to Poly-I:C-treated mothers displayed a significant increase in D1R immunoreactivity in the CPu specifically at adult age in comparison with adult offspring born to vehicle-treated control mothers. *p < 0.05, based on Fisher's LSD post hoc group comparison of PND70 specimen following the presence of a significant two-way interaction in the initial 2 × 3 (prenatal treatment × age) ANOVA (F(2,63) = 3.94, p < 0.05). B, Prenatal Poly-I:C exposure also significantly increased D1R immunoreactivity in the NAc shell but not in the core subregion in the adult offspring relative to adult control offspring. *p < 0.05, based on Fisher's post hoc group comparison of PND70 specimen following the presence of a significant two-way interaction in the initial 2 × 2 (prenatal treatment × postnatal age) ANOVA (F(1,42) = 3.31, p < 0.05). C, Representative images of coronal brain sections of adult (PND70) offspring born to vehicle- or Poly-I:C-treated mothers stained for D1R by immunohistochemistry. 1, CPu; 2A, NAc core; 2B, NAc shell. Scale bar, 500 μm. All values in A and B are means ± SEM. The numbers of offspring included in the analyses were N(GD19-vehicle) = 12, N(GD19-Poly-I:C) = 11, N(PND35-vehicle) = 12, N(PND35-Poly-I:C) = 11, N(PND70-vehicle) = 11, N(PND70-Poly-I:C) = 12.