Figure 7.
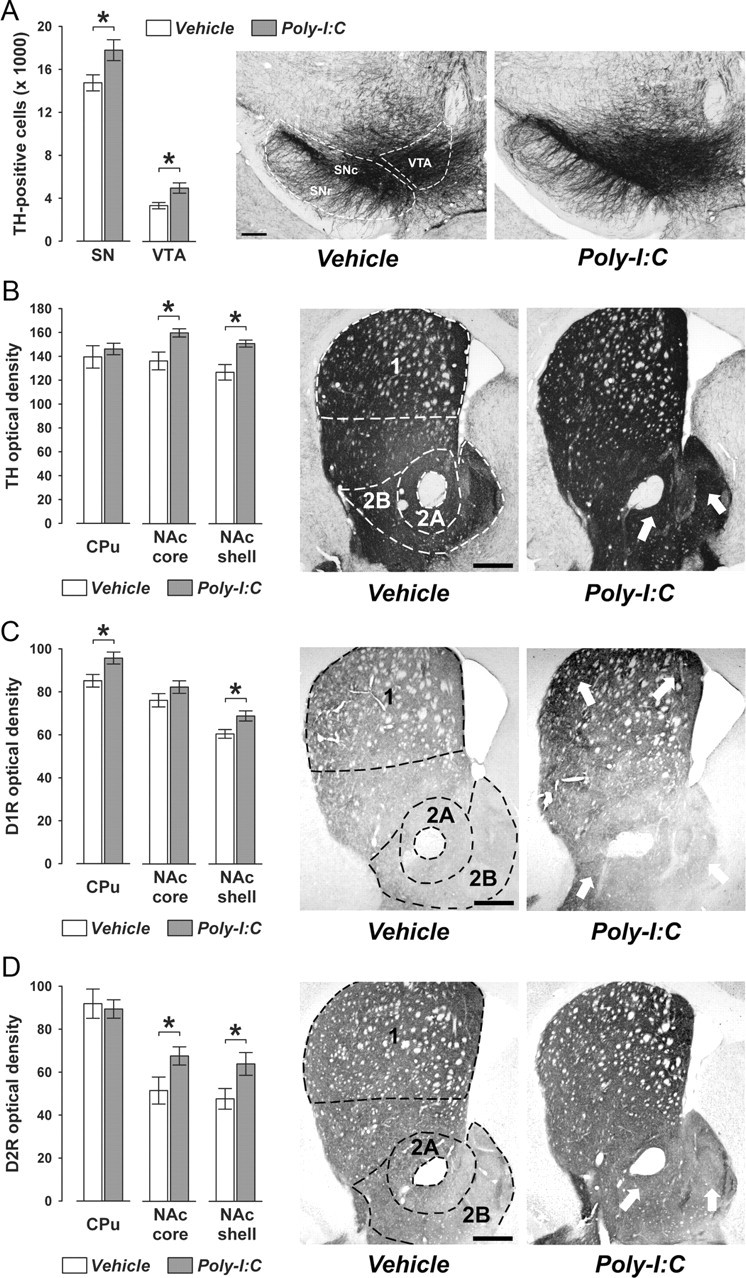
Confirmation of the adult dopaminergic phenotype in perfused adult brain samples. Pregnant mice were exposed to the viral mimic Poly-I:C or vehicle treatment, and immunoreactivities of TH, DAT, D1R, and D2R were assessed in the adult (PND70) offspring according to standard procedures using perfused brain samples. A, Prenatal Poly-I:C exposure led to a significant increase in the number of TH-positive cells in the SN (including both SNc and SNr) and the VTA compared with prenatal vehicle treatment. B, Offspring born to Poly-I:C-treated mothers displayed enhanced TH immunoreactivity specifically in the nucleus accumbens core (NAc core) and shell (NAc shell) subregions (indicated by the white arrows) but not in the CPu. C, Prenatal Poly-I:C exposure led to a significant increase in D1R immunoreactivity in the CPu and NAc core regions of the striatum (indicated by the white arrows) relative to prenatal control treatment. D, Offspring born to Poly-I:C-exposed mothers displayed enhanced D2R immunoreactivity specifically in the NAc core NAc shell subregions (indicated by the white arrows) but not in the CPu. All values are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, based on independent Student's t tests (two tailed). For all analyses, the numbers of offspring included in the analyses were N(vehicle) = 8, N(Poly-I:C) = 7. 1, CPu; 2A, NAc core; 2B, NAc shell. Scale bars, 250 μm.
