Figure 2.
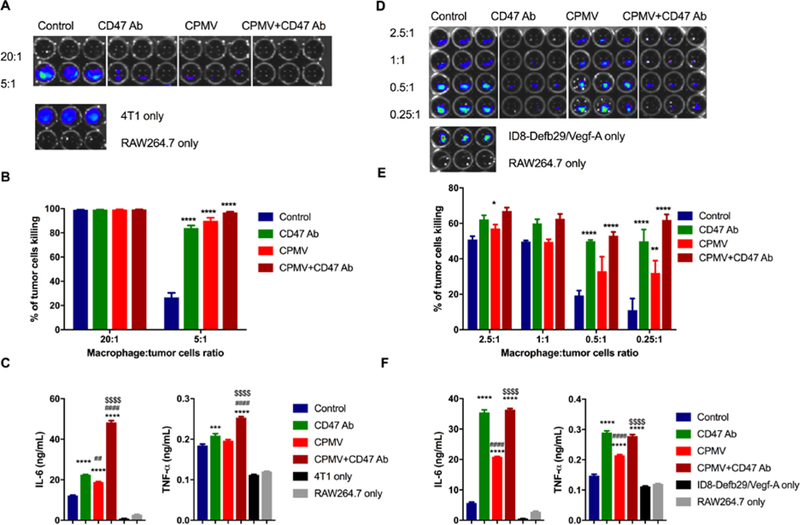
Tumor cytotoxicity improved by CD47 antibody blockade and CPMV. Murine macrophage (RAW 264.7) were co-cultured with mammary fat pad cells (4T1-Luc, A) and ovarian tumor cells (ID8-Defb29/Vegf-A-Luc, D) with different ratio, from 20:1 to 0.25 :1. 10 μg CPMV, anti-CD47 Ab or combination were added as treatment for 20 h. Bioluminescence intensity (BLI) was measured to quantify the percentage of live/dead 4T1 cells (B) and ID8-Defb29/Vegf-A cells (E) by phagocytosis. Data are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *vs. control. *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. At ratio 2.5:1 (4T1: RAW 264.7, C; ID8-Defb29/Vegf-A: RAW 264.7, F), the supernatant of each well was collected and released cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) were measured using ELISA. Data are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *vs. control; #vs. CD47 antibody; $vs. CPMV. ***p<0.0005, ****p<0.0001.
