Figure 1.
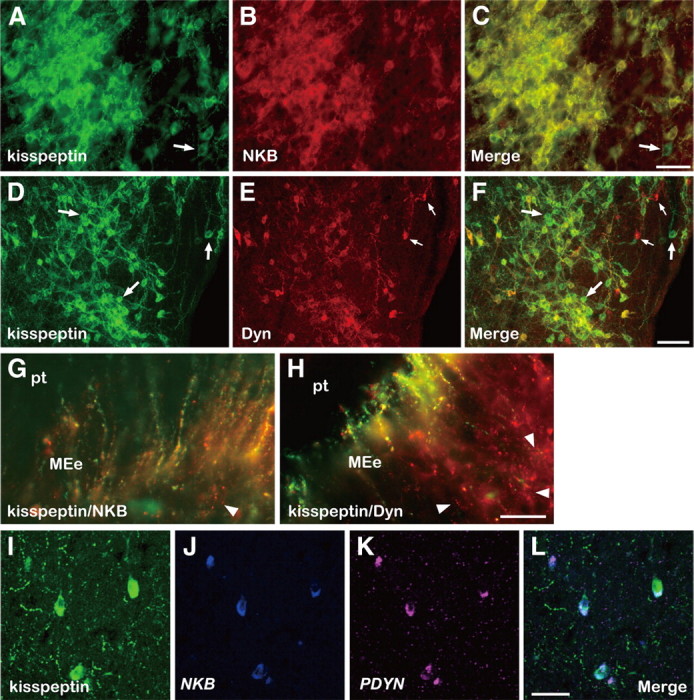
Colocalization of kisspeptin, NKB, and Dyn in the caudal ARC and ME of the goat. Photomicrographs of sections of the ARC stained by immunocytochemistry for kisspeptin (A) and NKB (B), or kisspeptin (D) and Dyn (E), are shown. C and F are computer-aid merged images of A and B, or D and E, respectively. An arrow in A or C indicates a cell body containing immunoreactivity (ir) for kisspeptin but not NKB-ir. The large arrows in D or F, or small arrows in E or F, show some cell bodies containing exclusively kisspeptin-ir or Dyn-ir, respectively. Note that numerous kisspeptin/NKB- or kisspeptin/Dyn-positive fibers surround immunopositive cell bodies. G and H are merged images of sections of the ME double stained for kisspeptin/NKB or kisspeptin/Dyn, respectively. The arrowhead in G indicates a fiber with only NKB-ir. The arrowheads in H show fibers with exclusively Dyn-ir. I–K show kisspeptin-ir and positive signals for NKB and PDYN in triple-label histochemistry, respectively. L is a merged image of I–K. MEe, External layer of median eminence; pt, pars tuberalis. Scale bars: A–C, I–L, 50 μm; D–F, 100 μm; G, H, 25 μm.
