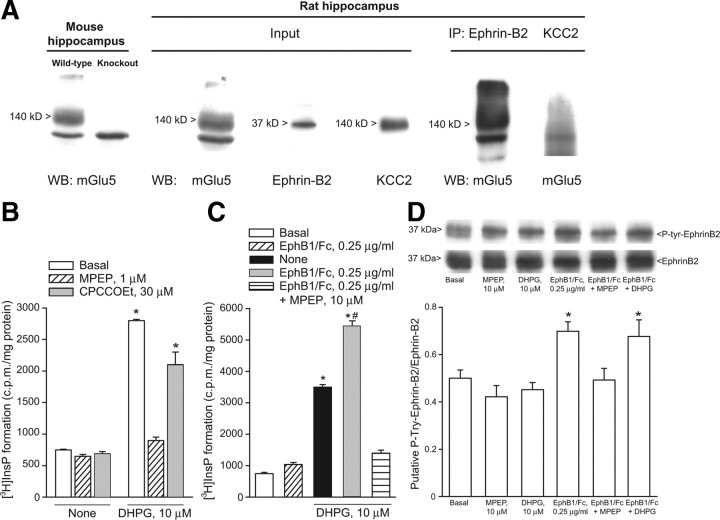
Figure 3.
A, mGlu5 receptors coimmunoprecipitate with ephrin-B2 in hippocampal protein extracts. From the left side: (1) expression of mGlu5 receptors in the hippocampus of adult wild-type or mGlu5 knock-out mice; (2) expression of mGlu5 receptors, ephrin-B2, and KCC2 in protein extracts from the hippocampus of 7- to 9-d-old rats used for immunoprecipitation (input); and (3) expression of mGlu5 receptors in ephrin-B2 immunoprecipitates, but not in KCC2 immunoprecipitates. IP, immunoprecipitates; WB, Western blotting. B, C, Stimulation of PI hydrolysis in neonate hippocampal slices challenged with DHPG (10 μm) in the absence or presence of CPCCOEt (10 μm) or MPEP (1 μm) or in the absence or presence of EphB1/Fc with or without MPEP is shown in B and C, respectively. Data are means ± SEM of 5–6 determinations. p < 0.05 [(one-way ANOVA + Tukey's PLSD) vs the respective values obtained in the absence of DHPG (*) or vs values obtained with DHPG alone (#)]. Tyrosine phosphorylation in ephrin-B2 immunoprecipitates from neonate hippocampal slices challenged with clustered EphB1/Fc, DHPG, or MPEP applied alone or in combination is shown in D. Data were normalized by the levels of total ephrin-B2 in immunoprecipitates. Densitometric values are means ± SEM of 4–5 determinations. *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA + PLSD vs control values).