Figure 2.
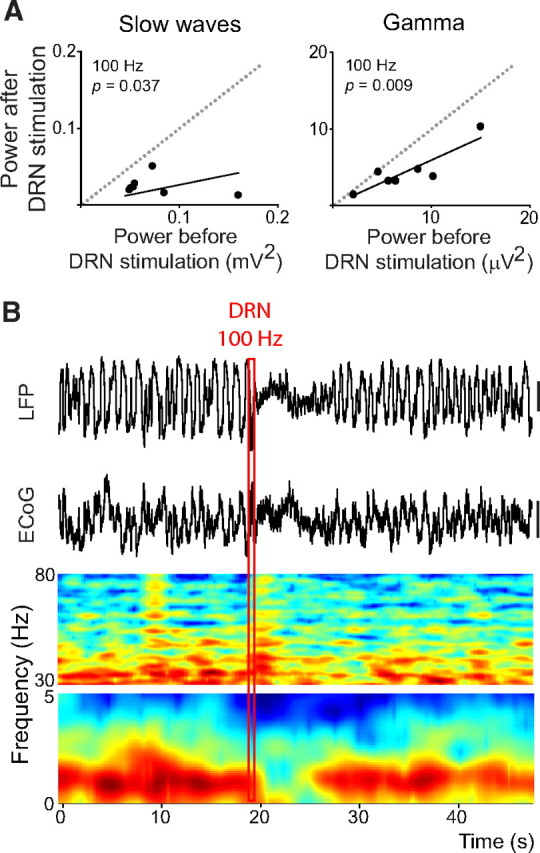
High-frequency stimulation of the DRN (100 Hz) strongly desynchronizes cortical slow waves and reduces gamma power. A, Stimulations of the DRN at 100 Hz (400 μA for 0.5 s) decrease the power of both slow and gamma oscillations in the LFP signal (comparison of 10 s epochs before and after the stimulations; n = 7 rats). B, The stimulation rapidly eliminates slow waves for several seconds in both the LFP and ECoG signals (top). Time–frequency analysis of the LFP reveals the disappearance of the slow-wave band and a reduction of the power of gamma waves (bottom). Spectrograms are normalized PSDs (in decibels), smoothed with a Gaussian filter. The red rectangle depicts the time of the stimulation and contains the stimulus artifacts in all the signals. Vertical bars are 0.5 mV.
