Figure 7.
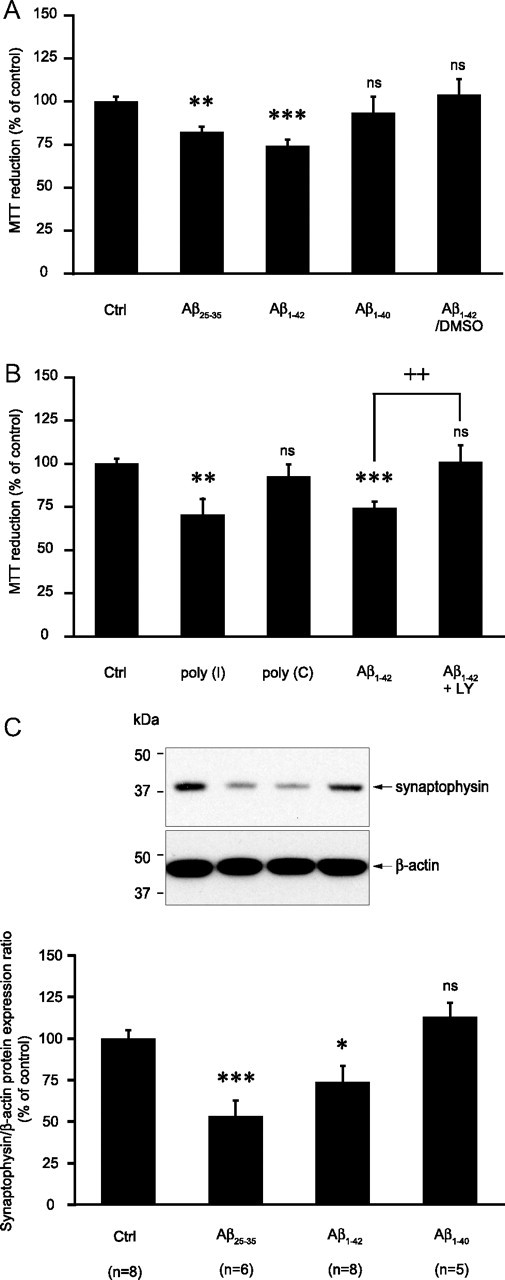
Impact of amyloid peptide treatment in astrocytes on neuronal viability in coculture. A–C, Astrocytes were stimulated with Aβ25-35 (25 μm), Aβ1-40 (10 μm), Aβ1-42 (10 μm), poly(I) (500 μg/ml), or poly(C) (500 μg/ml) (stock solutions in water) or with Aβ1-42 (10 μm) (stock solution in DMSO) (Aβ1-42/DMSO) for 24 h. Cells were then rinsed and the coculture was initiated by adding neurons seeded on glass coverslips on top of the astrocytic layer. Twenty-four hours later neuronal viability was determined using the MTT reduction assay (A, B) or neuronal proteins were harvested and synaptophysin expression was assessed by Western blotting (C). A, Isoform and structure dependency. Results are expressed as percentage of control (Ctrl) values and are means ± SEM of at least eight determinations from three independent experiments. B, Implication of SR-A receptors and the PI3-kinase cascade. When indicated, 10 μm LY294002 (LY) was added 1 h before and maintained throughout the whole incubation with Aβ1-42. Results are expressed as percentage of Ctrl values and are means ± SEM of at least 11 determinations from four independent experiments. C, Impact of amyloid peptides pretreatment in astrocytes on neuronal synaptophysin expression in cocultures. Representative Western blot bands are shown. Optical density measurements were used for quantification and values for synaptophysin were normalized using the corresponding β-actin value for each lane. Results are expressed as percentage of Ctrl values and are means ± SEM of at least five determinations from at least three independent experiments. Data obtained in A–C were statistically analyzed with ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's test (***p < 0.001 vs Ctrl; **p < 0.01 vs Ctrl; *p < 0.05 vs Ctrl; ++p < 0.01 vs Aβ1-42; ns, not significantly different from Ctrl).
