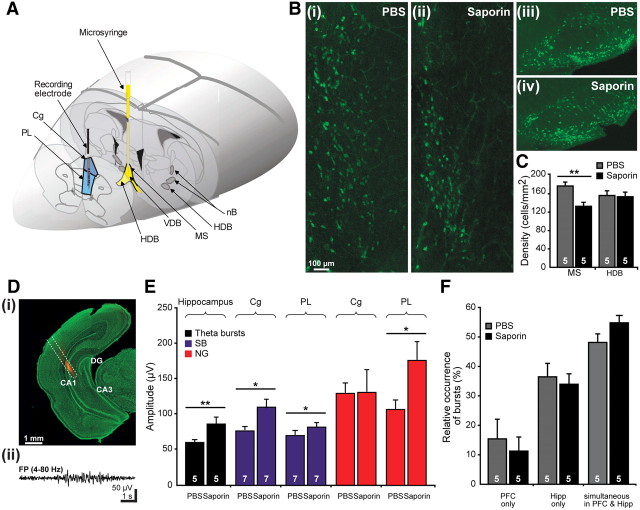
Figure 4.
Consequences of selective immunotoxic lesion of the cholinergic MS on the activity patterns within the prefrontal-hippocampal network. A, Scheme of experimental setup for recording the PFC (blue) and impairing some cholinergic nuclei (yellow). The spared cholinergic nuclei are marked in dark gray. B, Immunohistochemistry of ChAT-positive neurons in the MS (i, ii) and in the HDB (iii, iv) of PBS-treated (i, iii), and SAP-treated (ii, iv) pups. The pups were injected at P0 and investigated at P7. Note the decreased number of cholinergic neurons in the MS but not HDB of SAP-treated pups when compared with PBS-treated rats. C, Bar diagram displaying the density of ChAT-positive neurons in the MS and HDB of five PBS-treated (gray) and five SAP-lesioned (black) pups. Di, Digital photomontage reconstructing the location of the DiI-covered recording electrode (orange) in the intermediate Hipp of a Nissl-stained 50-μm-thick coronal section (green) from a P7 rat. Dii, Characteristic theta burst recorded in the CA1 area of the intermediate Hipp of a P7 rat and displayed after bandpass filtering (4–80 Hz). E, Consequences of SAP treatment on the prefrontal and hippocampal patterns of neonatal activity. Bar diagram displaying the mean amplitude of hippocampal theta bursts as well as of SB (blue) and NG (red) in the Cg and PL of PBS- and SAP-treated pups. The white numbers on the bars correspond to the number of investigated pups. F, Effects of SAP treatment on the temporal coupling of hippocampal and prefrontal activity. Bar diagram displaying the relative occurrence of oscillatory events that are present either exclusively in the PFC or in the Hipp or simultaneously in both regions of PBS-treated (gray) and SAP-treated (black) pups.