FIG. 1.
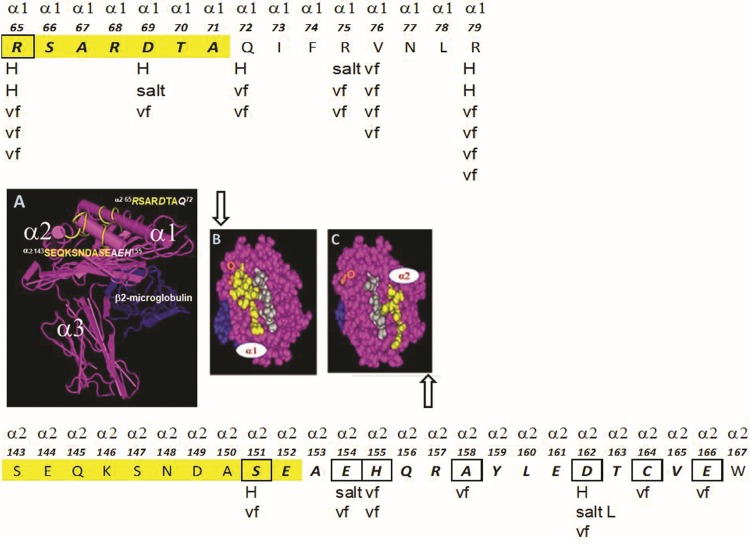
The structure of the nonclassical (HLA class-Ib) human leukocyte antigen HLA-E. (A) The structural orientation of the three α-helices of the heavy chain with β2m is illustrated. The peptide in the groove is not shown for the purpose of indicating the location of the specific amino acid sequences or epitopes on the α1 and α2 helices, which serve as the ligand for monospecific anti-HLA-E mAbs and CD94 and NKG2a receptors on the cell surface of NK cells and CD8+ T cells. The sequences in yellow in (A–C) are the specific sites of the ligand for mAb TFL-033, assessed based on dosimetric peptide inhibition studies. (A) The structure of intact or native HLA-E showing epitopes (the specific amino acid sequences) that inhibit the binding of mAb TFL-033 to HLA-E coated on the beads. The sequences RSARDTA at α1 and SEQKSNDASE at α2 are the TFL-033 binding regions established based on the peptide-inhibition study.(54) (B, C) The structure of the amino acids in the α1 and α2 helices that are recognized by CD94 and NKG2A. The letters H, Salt, and vf refer to the sites of hydrogen bonding, salt linkages, and van der Wall forces between CD94 and NG2A with the α1 and α2 helices, respectively. Gray of amino acid sequences refers to the sequences of the leader peptide sequence attached to the groove. The attachment of the peptide on the groove renders stability to dimerization of HLA-E heavy chains and β2m. Theoretically if a mAb binds anywhere in the yellow regions on the α1 and α2 helices, it would block the binding of the inhibitory receptor of NK cells. This is the basis for the hypothesis that monospecific anti-HLA-E mAbs define the potential of the mAb to avert the interaction between inhibitory receptors and HLA-E, and thereby preventing the “inaction” or “switching off” of the NK cell function that would otherwise enable tumor cell escape. The boxes refer to the exact amino acids in HLA-E sequences that interact or bind with the amino acids of CD94 and NKG2A. The linkgage types are shown in letters below the boxes. β2m, β2-microglobulin; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; mAb, monoclonal antibody; NK, natural killer; NKG2, natural killer cell group 2.