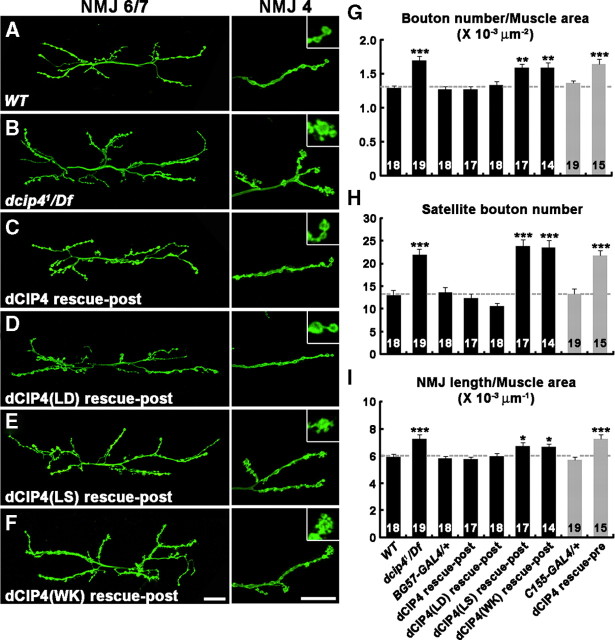
Figure 2.
Loss of postsynaptic dcip4 function leads to synaptic overgrowth. A–F, Confocal images of NMJs 6/7 (left) and NMJs 4 (right) of larval abdominal segment 2, stained for the neuronal membrane marker HRP. Insets show higher-magnification images of boutons, indicated by single asterisks. Compared with wild-type NMJs (A), dcip41/Df(3L)ED4342 mutant NMJs (B) exhibit an increase in total bouton number, satellite bouton formation, and total NMJ length. This phenotype is rescued by postsynaptic expression of dCIP4 [dCIP4 rescue-post: BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4,Df(3L)ED4342; C] and dCIP4–L145D [dCIP4(LD) rescue-post: BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–L145D,Df(3L)ED4342; D], but not by dCIP4–L436S [dCIP4(LS) rescue-post: BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–L436S,Df(3L)ED4342; E] and dCIP4–W603K [dCIP4(WK) rescue-post: BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–W603K,Df(3L)ED4342; F]. Scale bars, 25 μm. G–I, Quantification of bouton number (G), satellite bouton number (H), and NMJ length (I) at NMJ 6/7 in different genetic backgrounds. In G and I, measurements are normalized by the total surface area of muscles 6 and 7. The genotypes analyzed include wild-type (WT), BG57-GAL4/+, dcip41/Df(3L)ED4342 (dcip41/Df), BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4,Df(3L)ED4342 (dCIP4 rescue-post), BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–L145D,Df(3L)ED4342 [dCIP4(LD) rescue-post], BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–L436S,Df(3L)ED4342 [dCIP4(LS) rescue-post], BG57-GAL4,dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4–W603K,Df(3L)ED4342 [dCIP4(WK) rescue-post], C155-GAL4/+, and C155-GAL4/+; dcip41/UAS-HA-dcip4,Df(3L)ED4342 (dCIP4 rescue-pre). The number of NMJs quantified for each genotype is indicated inside the bars. Statistically significant differences versus wild-type are marked on top of bars (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Raw data are shown in supplemental Table 1 (available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material).