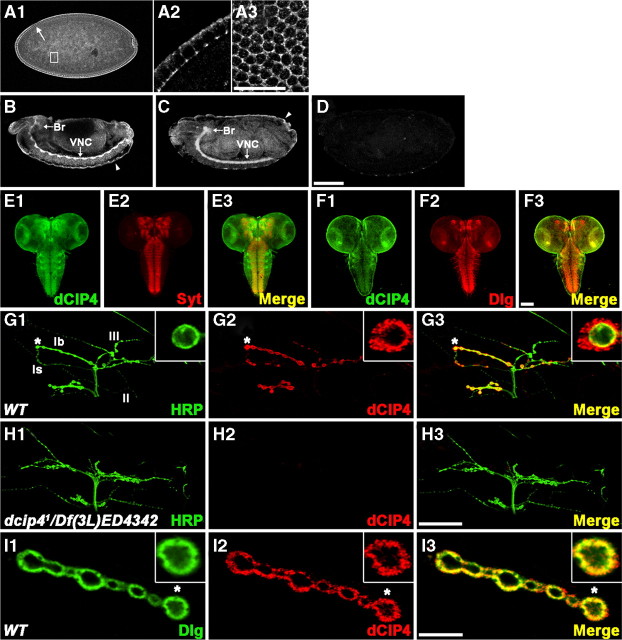
Figure 3.
dCIP4 expression in the CNS and at the NMJ. A1–A3, Lateral view of a late stage 5 wild-type embryo stained with anti-dCIP4. Higher-magnification images of the areas indicated by the arrow and box in A1 are shown in A2 and A3, respectively. The image shown in A3 is a superficial optical section of an embryo. Note that the maternally derived dCIP4 protein is highly enriched at the cell borders. Dorsal is up, anterior is to the left. B, C, Lateral views of stage 13 (B) and 16 (C) wild-type embryos stained with anti-dCIP4. dCIP4 is highly concentrated in the brain (Br) and VNC and the surface epithelium (arrowheads). D, Lateral view of a stage 16 dcip41/Df(3L)ED4342 embryo stained with anti-dCIP4. E1–F3, Confocal images of the CNS dissected out of wild-type third instar larvae double stained with anti-dCIP4 (green) and either anti-Syt (red) or anti-Dlg (red). G1–H3, Confocal images of NMJs 12/13 double stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-dCIP4 (red). In wild-type larvae (G1–G3), dCIP4 immunoreactivity is detected only at type Ib and Is boutons and is absent at other types. Insets in G1–G3 show higher-magnification images of single Ib boutons labeled with asterisks. dcip41/Df(3L)ED4342 mutant larvae (H1–H3) lack detectable dCIP4 staining at the NMJ 12/13. I1–I3, A single confocal slice of an NMJ 6/7 branch with type Ib boutons double stained with anti-Dlg (green) and anti-dCIP4 (red). Insets show higher-magnification images of single boutons labeled with asterisks. Scale bars: (in A3) A2, A3, 10 μm; (in D) A1, B–D, 100 μm; (in F3) E1–F3, 100 μm; (in H3) G1–H3, 50 μm; (in I3) I1–I3, 10 μm.