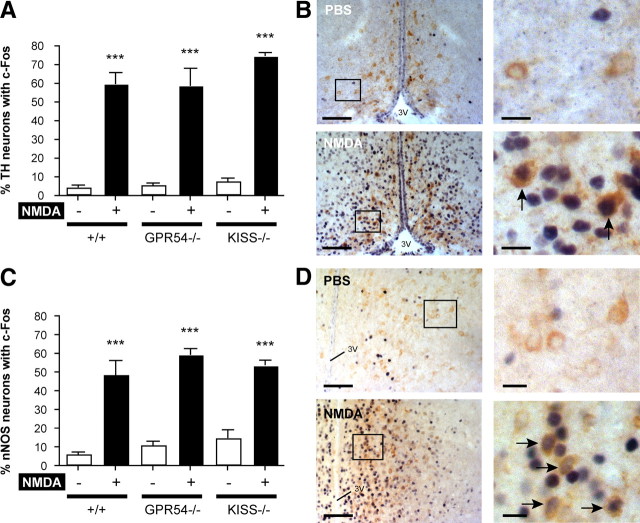
Figure 7.
Catecholamine- and nitric oxide-producing neurons are responsive to NMDA in Kiss1 and Gpr54 mutant mice. Catecholamine- and nitric oxide-producing neurons were immunostained for TH and nNOS, respectively. A, Bar graph showing the mean ± SEM percentage of TH neurons counted per section with c-Fos in the AVPV and PeN of wild-type (+/+), Kiss1-null (Kiss−/−), and Gpr54-null (Gpr54−/−) mice after PBS (−) or NMDA (+) intracerebroventricular injection. B, Representative dual-labeled immunocytochemistry showing TH (brown cytoplasmic staining) and c-Fos (dark blue nucleic staining) in the AVPV after PBS or NMDA. Arrows indicate TH neurons with c-Fos. C, Bar graph showing the mean ± SEM percentage of nNOS neurons counted per section with c-Fos in the AVPV, MnPO, MPO, MS, and OVLT of +/+, Kiss−/−, and Gpr54−/− mice after PBS (−) or NMDA (+) intracerebroventricular injection. D, Representative dual-labeled immunocytochemistry showing nNOS (brown cytoplasmic staining) and c-Fos (dark blue nucleic staining) in the MPO after PBS or NMDA. Arrows indicate nNOS neurons with c-Fos. Boxes indicate magnified views of photos on the right. 3V, Third ventricle. Scale bars: B, 125 μm at low magnification and 15 μm at high magnification; D, 150 μm at low magnification and 20 μm at high magnification. ***p < 0.001 versus PBS in same genotype (unpaired t test).