Figure 2.
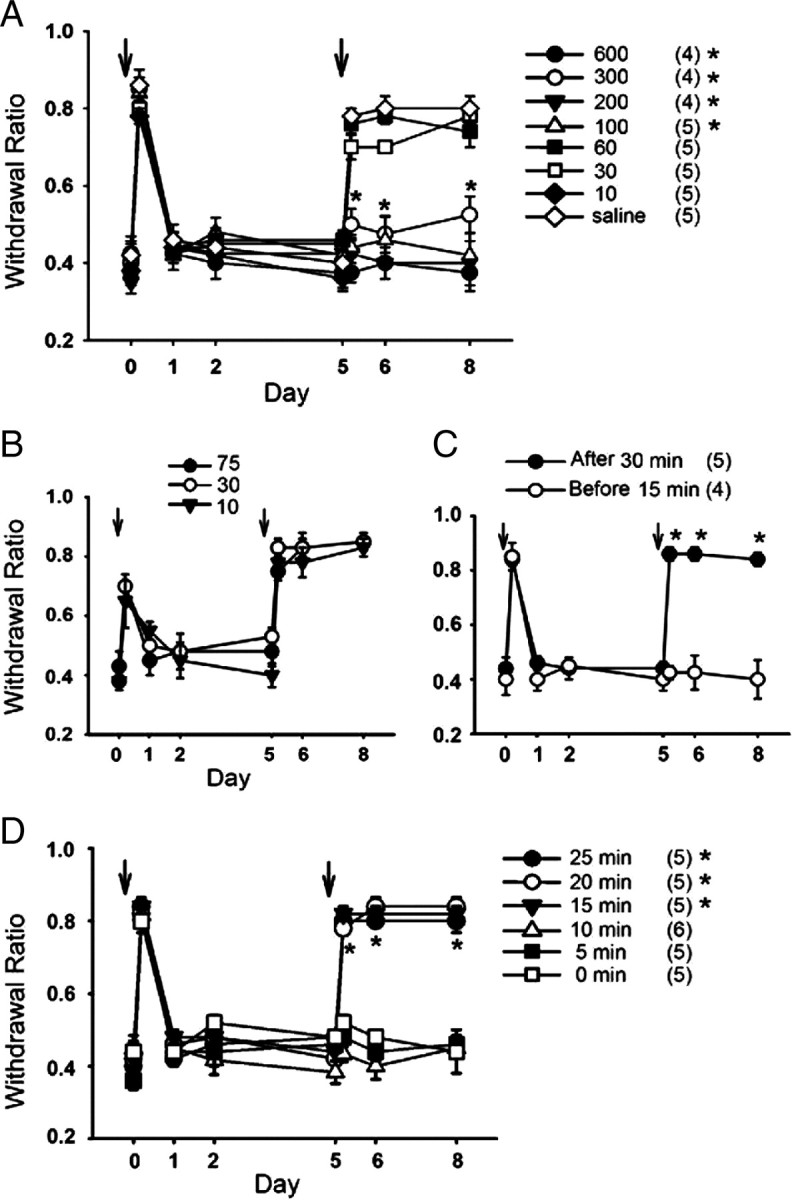
Blocking T-channels prevents the development of acid-induced chronic mechanical hyperalgesia in WT mice in a dose- and time-dependent manner. A, Effects of different dosages (in mg/kg) of ETX administered intraperitoneally. One hundred milligrams per kilogram is the lowest dosage tested that prevented hyperalgesia. *p < 0.05, compared with saline-treated animal. B, Effects of different dosages of the L-channel blocker nicardipine. None of the dosages tested had a significant effect on acid-induced hyperalgesia (n = 4). C, Effects of ETX injection before and after the second acid injection. Treatment with ETX 15 min before but not 30 min after the second acid injection prevented acid-induced chronic hyperalgesia. *p < 0.05, compared with group treated with ETX 15 min before acid injection. D, Effects of ETX administration at different time points (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 min) after the second acid injection. ETX given at 10 min (or less) after second acid injection prevented the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. In contrast, ETX given at 15 min (or more) after second acid injection had no effect on the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of animals tested. *p < 0.05, compared with 0 min group. Error bars represent SEM.
