Figure 1.
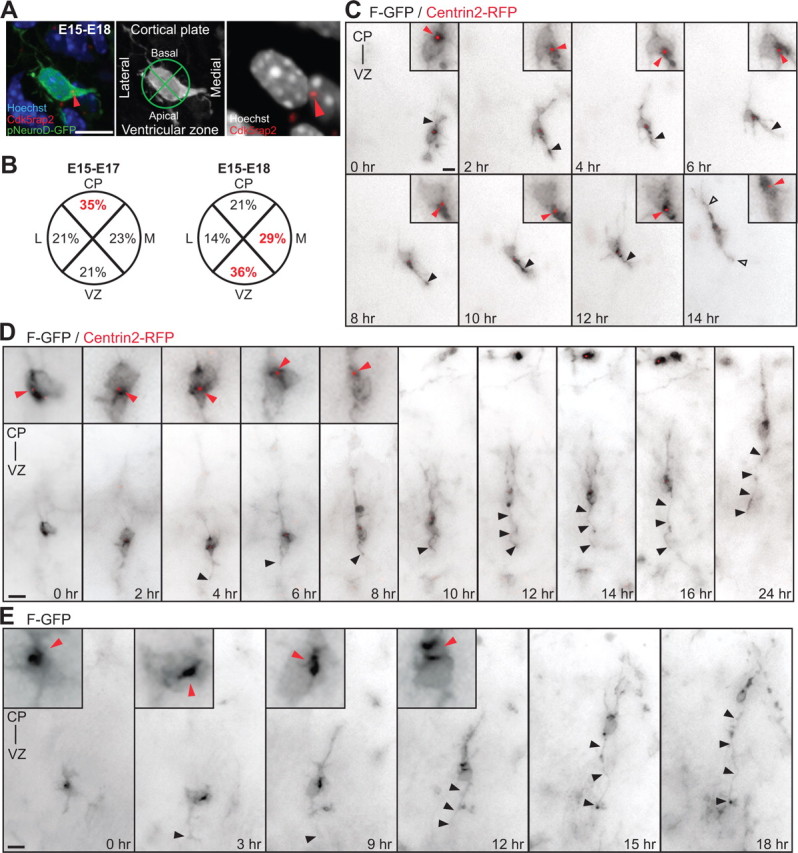
The centrosomes of multipolar neurons translocate toward the VZ in advance of axon formation. A, Multipolar neurons in the lower IZ, identified by pNeuroD-GFP expression, are labeled with Cdk5rap2 (red arrowhead) and Hoechst. Cell body centroid analysis is used to determine centrosome position (middle panel). B, Quantification of centrosome position at E17 and E18 in pNeuroD-GFP-positive multipolar neurons from E15 in utero electroporation. C, Time-lapse imaging of a multipolar cell expressing F-GFP and Centrin2-RFP (insets, red arrowhead). At 0 h, centrosome is oriented toward the CP. From 2 to 12 h, the centrosome orients toward the VZ and midline (6 h). The cell assumes a bipolar morphology (open arrowheads) with the centrosome toward the leading edge and the CP at 14 h. The apical neurite accumulates more membrane components when the centrosome is located at its base (black arrowhead). D, E, Multipolar cells form an axon before migration into the CP. D, Time-lapse imaging of a cell expressing F-GFP and Centrin2-RFP, with the centrosome toward the VZ before elongation of the axon (insets in 0 h-4 h, red arrowheads). The centrosome translocates toward the CP (red arrowheads, inset in 6 h-8 h) and the cell reassumes a bipolar morphology, leaving the growing axon behind (black arrowheads, 6 h-24 h). E, Inversion of the polarized cytoplasm (red arrowheads, inset in 0–12 h) in a cell expressing F-GFP toward the VZ before elongation of the axon (black arrowhead). Scale bars: A, C–E, 10 μm.
