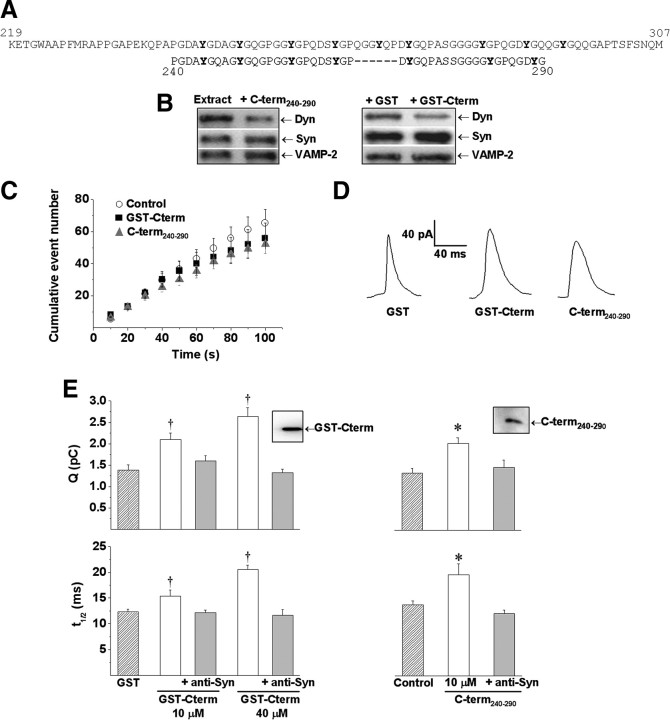
Figure 4.
Microinjections of synaptophysin C-terminal derivatives increase duration and quantal size of depolarization-induced exocytotic events. Chromaffin cells were injected with GST (40 μm), GST-Cterm (10 and 40 μm), GST-Cterm plus anti-Syn antibody (10 and 40 μm), C-term240-290 (10 μm), or C-term240-290 plus anti-Syn antibody (10 μm). Thirty to forty-five minutes after injections, exocytosis responses evoked by high K+ were measured. A, Amino acid sequence of the C-terminal domain of rat synaptophysin (top, gray) and the synthetic peptide C-term240-290 (bottom, black). Tyrosine residues are shown in bold. Underlined amino acids indicate the epitope recognized by anti-Syn. B, Protein extracts from chromaffin cells were immunoprecipitated with a polyclonal anti-synaptophysin antibody, in the presence of 10 μm C-term240-290, GST, or GST-Cterm. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against Syn, Dyn, and VAMP-2. C, Cumulative histograms of the number of amperometric events from control cells (white circles), cells injected with 40 μm GST-Cterm (black square) or 10 μm C-term240-290 (gray triangles). D, Representative amperometric traces from cells injected with GST, GST-Cterm or C-term240-290. E, Averaged values for Q and t1/2. Data are means ± SEM of averages per cell (12–24 cells from 3 to 5 different cultures). *p < 0.05 compared with control cells. Insets: Immunoblotting showing that GST-Cterm and C-term240-290 are recognized by the anti-Syn antibody.