Figure 3.
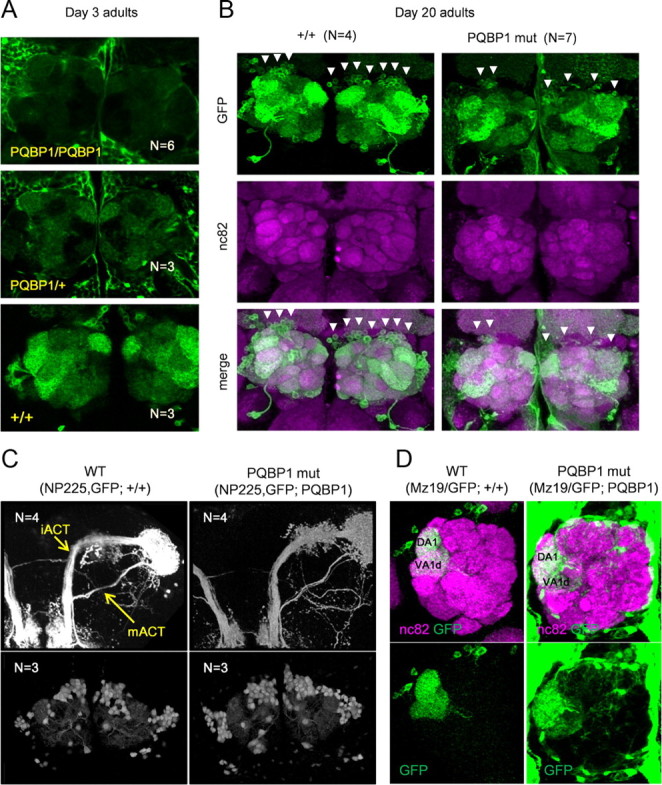
Effect of dPQBP1 reduction on PNs. mCD8-GFP was driven by projection neuron-specific drivers, GH146-Gal4 (A, B), and NP225 (C, D). A, At 3 d, GFP expression in the antennal glomeruli is reduced in homozygous (top) or heterozygous (middle) of dPQBP1 mutant compared with wild-type flies carrying normal dPQBP1 (bottom). B, Wild-type flies (left columns) and homozygous dPQBP1-mutant flies (right columns) at 20 d. Expression of GFP is also significantly reduced in PNs (arrowheads) of dPQBP1 mutants (top). Immunostains of nc82 are not changed in dPQBP1 mutants (middle), indicating that synapses of antennal glomeruli are normal in dPQBP1 mutants. The bottom columns show merged images. The green and magenta signals indicate GFP and nc82, respectively. The arrowheads indicate “visible” cell bodies. C, Axonal projection patterns (top) and cell body patterns (bottom) are similar between genotypes. Both NP225 driver and mCD8-GFP are homozygous. mACT and iACT are indicated by arrows. D, Confocal images of MZ19-Gal4 expression pattern show dendrite patterns (bottom) are similar between genotypes. MZ19-positive dendrites innervate DA1 and VA1d glomeruli in both WT and dPQBP1 mutant. The top panels show merged images of nc82 (magenta) and GFP (green), and the bottom panels show GFP only images. The green signals in the background of mutant indicate YFP driven by pax6 promoter in the piggyBac transposon.
