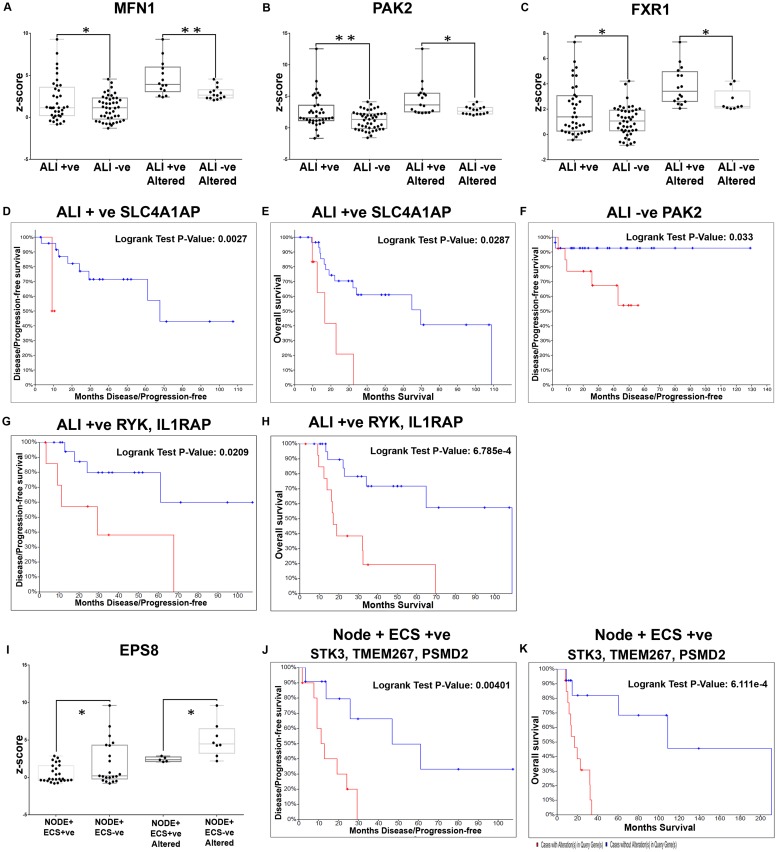
Fig 6. Molecular markers with significant differential expression and prognostic efficacy in laryngopharyngeal cancers with angiolymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis.
Validation of the differentials identified in the laryngopharyngeal cancer within the TCGA cohort of patients with angiolymphatic invasion identified 4 genes with significant difference in mRNA expression levels (z-score) in TCGA cohort laryngopharyngeal cancer with ALI; the top three genes being MFN1, PAK2 and FXR1 (A-C). Among this cohort, SLC4A1AP showed an association in both OS (D; p = 0.002785) and DFS (E; p = 0.0287) of ALI+ patients, while PAK2 showed association with ALI- in DFS alone (F; p = 0.033). Prognostic assessment of the subset of meta-analysis based differentials altered in >20% of the patients identified the combination of RYK and IL1RAP to be associated with poor survival (G and H). EPS8 was the only differential in node in node+ECS- patients with no survival impact (I) validation of the differentials associated with node positive with/without ECS indicated that EPS8 was the only differential (downregulated) in node+/ECS+ cohort with no association with survival. Prognostic efficacy (subset altered in >20% patients) indicated that STK3, TMEM267 and PSMD2 were the prognosticators of poor survival (J and K). (P-value; * p<0.05; ** p<0.005).