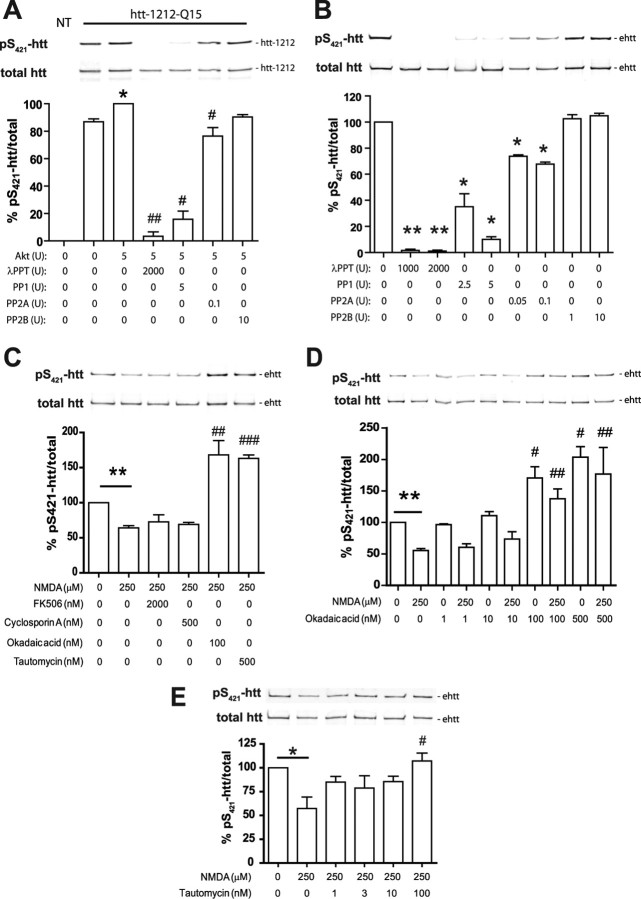
Figure 4.
Reduced levels of pS421-htt after excitotoxic NMDAR stimulation is attributable to enhanced PP1 and PP2A activity. A, Htt-1212-Q15 was expressed in COS7 cells, immunopurified with mAb 2166, and phosphorylated at S421 in the presence of Akt. Equimolar amounts of htt-1212-Q15 were treated with phosphatases for 30 min at the indicated concentrations and analyzed by Western blot followed by probing with Abs against pS421-htt and total htt (mAb 2166). *p < 0.05 compared without Akt (lane 2); #p < 0.05 compared with Akt (lane 3) by paired t test. B, Full-length htt was immunoprecipitated from cortical lysate harvested at 12 DIV and equimolar amounts of htt were phosphatase-treated as described in A. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005 compared with control by paired t test. C–E, Cortical neurons at 12 DIV were treated with 250 μm NMDA, 30 μm glycine for 10 min, or left untreated in the presence or absence of phosphatase inhibitors. After receptor stimulation, cultures were incubated for 15 min and processed for immunoprecipitation of htt and Western blot. Membranes were probed with Abs against pS421-htt and total htt (mAb 2166) followed by probing with secondary Abs and quantification. In all experiments, the ratio between pS421-htt and total htt was determined and expressed relative to controls in each of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005 compared with control by paired t test; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.005, and ###p < 0.005 compared with NMDA-treated cultures by t test. Error bars denote ±SEM.