Figure 6.
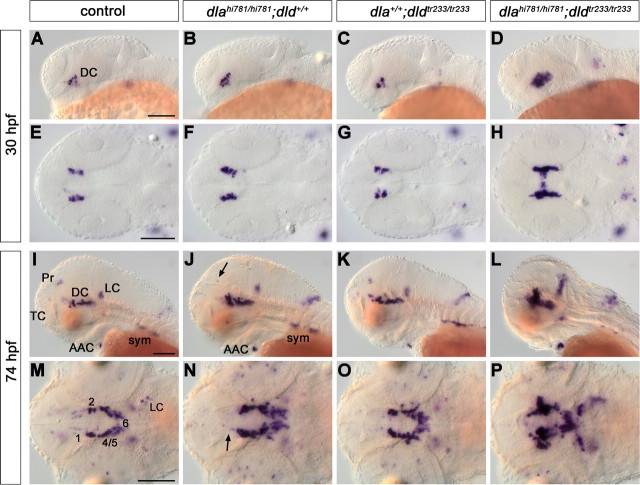
deltaA and deltaD mediate diencephalic DA neurogenesis. The formation of CA neurons was analyzed in the offspring of fish carrying both dlahi781 and dldtr233 mutant alleles. The embryos were stained for th expression by WISH at 30 (A–H) and 74 (I–P) hpf, and genotyped. Controls (A, E, I, M) are homozygous WT siblings. An increase of th-expressing ventral diencephalic cells was observed in dlahi781 mutants at 30 hpf (B, F). To estimate this increase, in a separate experiment the embryos were immunostained, imaged at the confocal microscope, and DA cells counted. By 30 hpf, wild-type siblings developed on average 27.4 DA neurons (N = 8), and dlahi781 mutant embryos 40.4 neurons (N = 7). At 74 hpf, th expression in dlahi781 mutants (J, N) was differentially affected: whereas cell numbers increase in DC2/4/5/6, a reduction in DC1 (N, arrow), Pr (J, arrow), and TC was observed. The formation of AAC and sympathetic ganglia was not affected (J). The phenotype of dldtr233 mutant embryos (C, G, K, O) showed only a minor increase of th-expressing cells in the ventral diencephalon (O). Conversely, the absence of both DeltaA and DeltaD activities in dlahi781/dldtr233 double-mutant embryos (D, H, L, P) resulted in a dramatic enhancement of the th phenotype, similar to the one observed in mind bomb mutants (Fig. 4). A–D, I–L, Lateral views. E–H, M–P, Dorsal views, anterior left. E–H and M–P are z-projections of transmitted light image stacks. Scale bars, 100 μm. For abbreviations, see Figure 4.