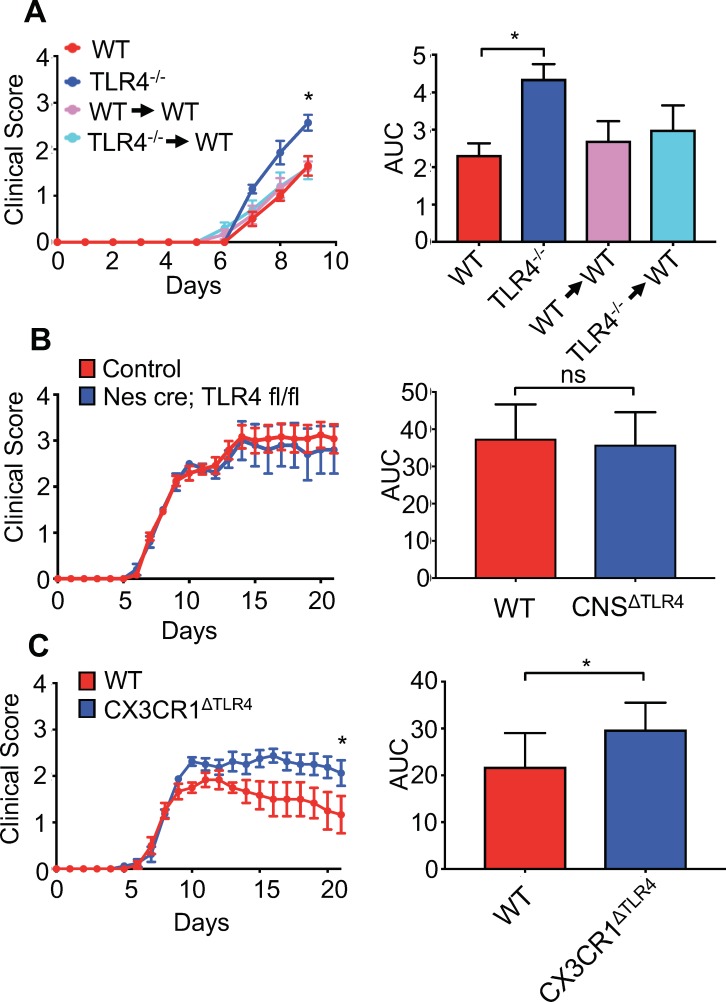
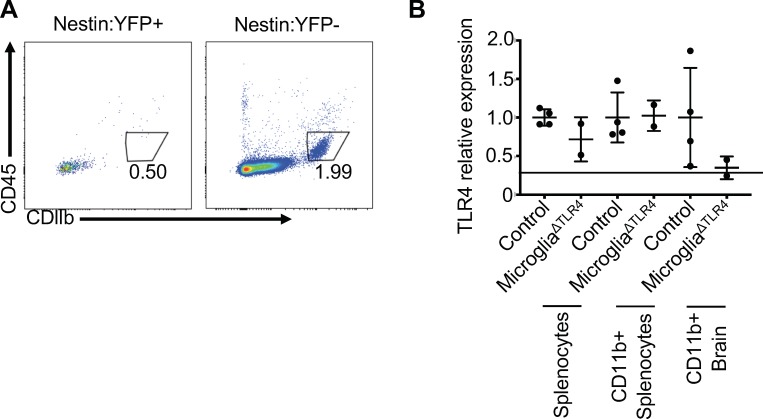
Figure 7. Microglial-specific TLR4 signaling protects from neurologic disease.
(A) WT, TLR4-/-, WT mice receiving WT bone marrow and WT mice receiving TLR4-/- bone marrow were infected with JHMV and clinical scores (left) and area under curve (right) calculated. (B) Nestin-Cre or TLR4-fl/fl (as WT controls) (n = 12) and nestin-Cre TLR4-fl/fl (n = 5) were infected with JHMV and clinical scores (left) and area under curve (right) determined. Results representative of two independent experiments (C) TLR4 fl/fl (n = 6) (as WT controls) and CX3CR1CreER TLR4 fl/fl (n = 8) mice were treated with tamoxifen, and 1 month later infected with 150 PFU of JHMV. Clinical scores (left) and area under curve were calculated. All data displayed as mean with SEM. Means are of biological replicates. Clinical score significance determined using two-way ANOVA statistical test with multiple comparisons. Area under the curve significance calculated by one-way ANOVA, comparing each group to WT (B) or by Student’s t test (C). *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.