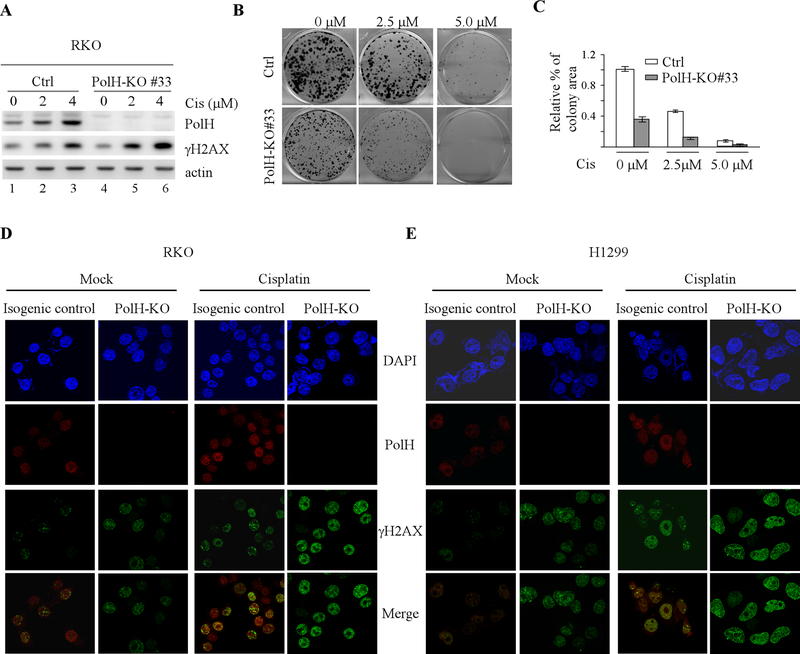
Figure 3. Loss of PolH leads to enhanced DNA damage response.
(A) Isogenic control and PolH-KO RKO cells were treated with or without cisplatin (2.5 uM) for 18 h, followed by western blot analysis to examine the level of PolH, γ-H2AX, and actin. (B) Colony formation assay was performed using isogenic control and PolH-KO RKO cells treated with or without cisplatin for 18h. (C) Quantification of colony formation assays in B. (D-E) Immunofluorescence assay was performed with isogenic control and PolH-KO RKO (D) and H1299 (E) cells treated with or without cisplatin (2.5 uM, 8h). The PolH (red) image was obtained by anti-PolH and Texas red-conjugated secondary antibody. The γ-H2AX (green) image was obtained by anti-γ-H2AX and FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. The immunofluorescence images was captured using were obtained using a 63x oil objective of the Leica TCS SP8 confocal microscope.