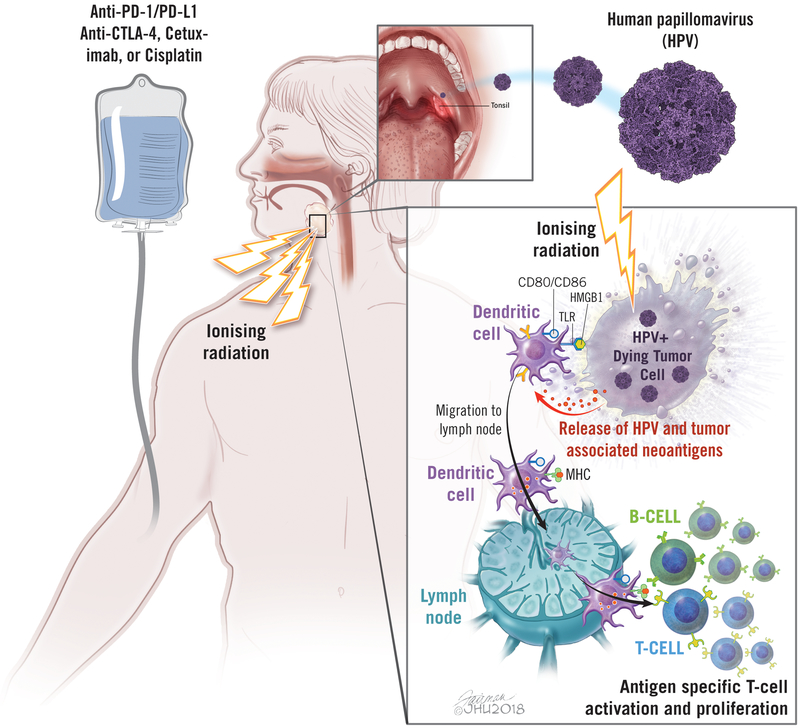
Figure 1. Radiation-induced immune responses in head and neck cancer.
Radiation induces 1) release of tumor antigens and damage-associated molecular pattern (e.g. HMGB1) via cell death, 2) activation and migration of dendritic cells to lymph node, 3) enhanced cross-presentation of tumor antigens via upregulation of MHC I, and 4) antigen-specific T cell activation and proliferation. Radiation therapy can be combined with immunotherapy (checkpoint blockade) or chemotherapy. TLR: toll-like receptor, HMGB1: high mobility group protein B1, MHC: major histocompatibility complex, PD-1: programmed cell death-1