Fig. 2.
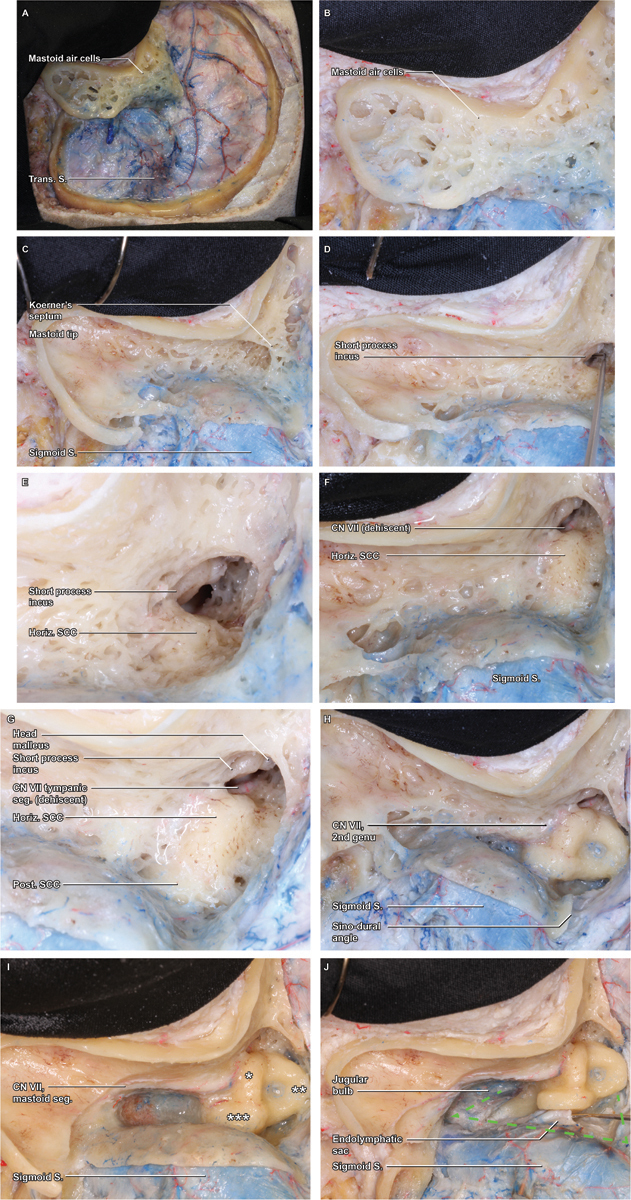
Mastoidectomy. ( A ) With the craniotomy flap removed, attention can be turned to the mastoidectomy, which is initiated by removal of the superficial cortex with a large cutting burr. ( B ) A detail view demonstrates the thin cortical rim circumscribing the cortex, which will be the boundary of the ensuing bone removal. ( C ) As the superficial mastoid air cells are removed, the broad saucer of the mastoid cortex is outlined, as is the deep limit of thin cortical bone overlying the sigmoid sinus. The mastoid air cells coalesce in the antrum, which is obscured by Koerner's septum, the last layer of medullary bone removed during the superficial mastoidectomy. ( D ) Within the antrum, the short process of the incus is visualized, a key landmark that points toward the mastoid genu of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). ( E ) As the floor of the antrum is exposed, a thin rim of dense, yellow otic capsule bone emerges, indicating the lateral curve of the horizontal semicircular canal (SCC). ( F ) Removal of the final mastoid trabeculae fully reveals the curvature of the horizontal SCC, beyond which the tympanic segment of the facial nerve may be appreciable, if the normal bony covering is dehiscent ( G ) As bone removal proceeds along the curve of the horizontal SCC, the otic capsule bone of the posterior SCC is revealed in a perpendicular orientation, medial and posterior. ( H ) Still further dissection along the superior arc of the posterior canal leads to the common crus, where the posterior and superior canals coalesce at the superomedial corner of the bony labyrinth. Maximizing bone removal by carefully skeletonizing this corner of the labyrinth is a critical means of optimizing the exposure. ( I ) Inferior to the horizontal SCC and lateral to the posterior SCC, the facial nerve (VII) within the fallopian canal is skeletonized and traced inferiorly through its mastoid segment. ( J ) With the course of CN VII clearly identified, completion of the bony dissection can be rapidly completed, exposing the jugular bulb, sigmoid sinus, and superior petrosal sinus—the anatomical boundaries of Trautman's dural triangle.
