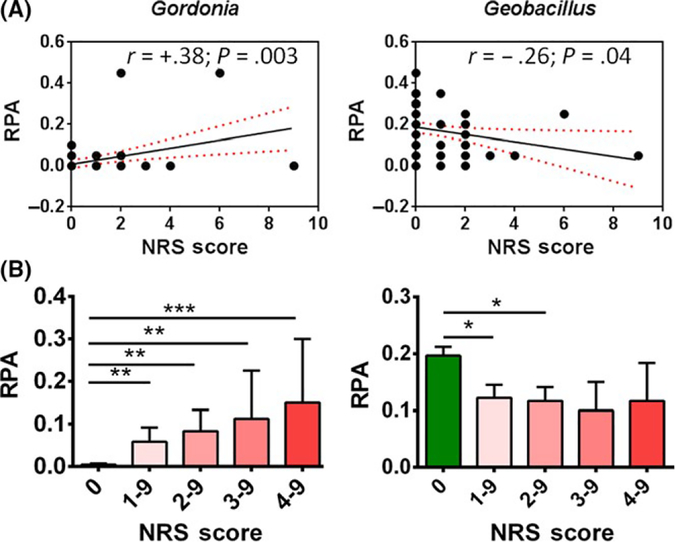
FIGURE 2.
Facial skin bacterial microbiome correlates with NRS score. (A) The positive and negative correlation of relative percentage abundance (RPA; closed dots) of bacterial microbiome genera (Gordonia and Geobacillus) with NRS score displayed. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r), and p-values, and linear regression line fitting the data (black solid line) with 95% confidence interval (red dotted line) are shown on each graph. n = 60 (n = 42 (no rosacea); n = 18 (rosacea)). There are several closed dots that overlap with each other. Therefore, the number of total dots appears less than total number of sample. (B) Relative percentage abundance (RPA) of Gordonia and Geobacillus for subjects with “No Rosacea (subjects with NRS score = 0)” and “Rosacea (subjects with score NRS score = 1–9)” was plotted with increasing NRS score. The difference in mean of RPA between no rosacea and rosacea is greater with increasing NRS score. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of n = 42 (NRS score = 0), 18 (NRS score = 1–9), 12 (NRS score=2–9), 4 (NRS score=3–9) and 3 (NRS score = 4–9). p-values for no rosacea vs. rosacea are shown as *<.05; **<.001; ***<.0001. NRS, National Rosacea Society measured for severity of rosacea