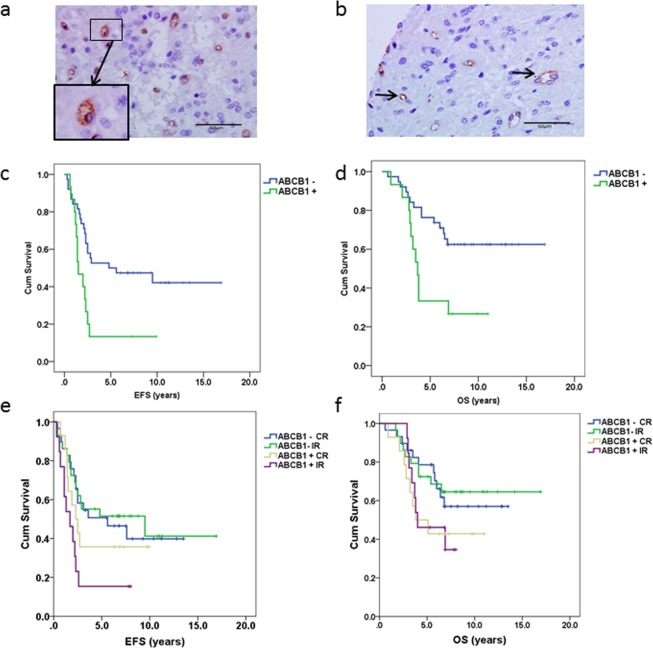
Figure 4.
Membranous expression of ABCB1 was associated with poor survival and early relapse in ependymoma. Tissue microarrays from the CNS9204 clinical trial cohort were screened for ABCB1 protein expression. (a) An ependymoma patient sample in which a sub-population of tumour cells stained positive for membranous ABCB1 expression (boxed and magnified). (b) Ependymoma samples which demonstrated vascular staining (arrows) in the absence of membranous staining tumour cells were scored as negative. Scale bars represent 50 µm. (c) ABCB1 positive patients from the chemotherapy-led (CNS9204) trial had a significantly reduced event-free survival (5-year EFS 13% vs. 50%, p = 0.007). (d) Overall survival was also significantly reduced in ABCB1 positive CNS9204 patients (5-year OS 33% vs. 74%, p = 0.009) respectively. Data from both trials were combined in order to explore the potential effect modification between ABCB1 and resection status. e. Patients with an incomplete resection who were ABCB1 positive had the poorest EFS (5-year EFS- 15%, p = 0.03) in comparison to other groups. (f) Overall survival was not significantly correlated with resection status although patients who were ABCB1 positive had the worst prognosis. CR complete resection, IR incomplete resection, +censored.