Figure 4.
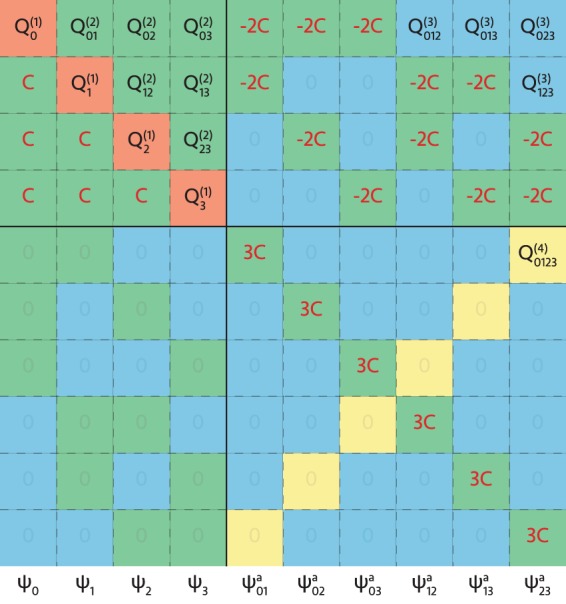
Example QUBO for a system of second-order polynomial equations. The QUBO can be organized into four quadrants as indicated by the solid black lines, corresponding to bilinear (2nd quadrant), tri-linear (1st and 3rd quadrants) and quadra-linear (4th quadrant) contributions. Within the quadrants, the elements are colored to reflect the effective one (red), two (green), three (blue), and four (yellow) qubit interactions after accounting for repeated indices. The entries in are distributed to entries in the QUBO corresponding to the order of interaction: Q(1) to red, Q(2) to green, Q(3) to blue, Q(4) to yellow. The coefficients of the constraint equations contributes to entries in red text.
