Figure 9.
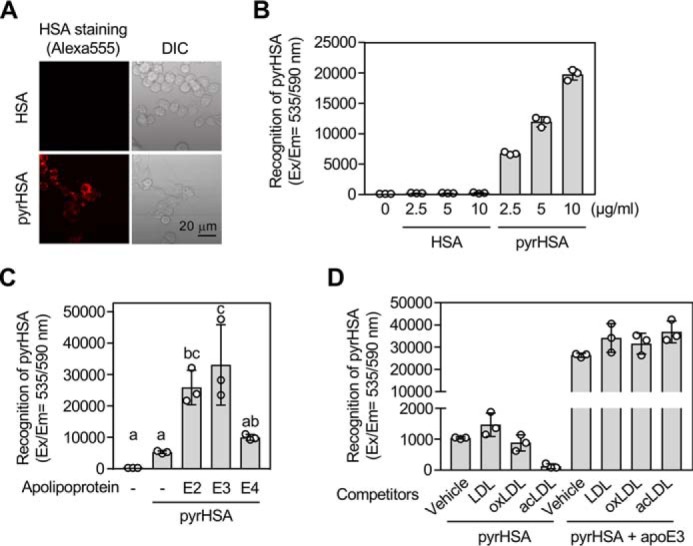
apoE3 enhances cellular recognition of pyrrolated proteins. A and B, binding/uptake of pyrHSA in RAW264.7 cells. A, representative fluorescence microscopy images of the cells treated with 1 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled HSA (upper panels) or 1 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled pyrHSA (lower panels) for 1 h. Left, Alexa Fluor® 555; right panels, brightfield. DIC, differential interference contrast. B, the cells were treated with 0–10 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled HSA (n = 3) or Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled pyrHSA (n = 3) for 1 h. The results shown are means ± S.D. (n = 3). C, effect of apolipoproteins on binding/uptake of pyrHSA. RAW264.7 cells were treated with 10 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled pyrHSA together with or without 50 μg/ml of apoE (apoE2, apoE3, or apoE4) for 1 h. The results shown are means ± S.D. (n = 3). The differences were analyzed by Tukey's HSD test. Different letters above bars indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05). D, effect of lipoproteins on binding/uptake of pyrHSA in RAW264.7 cells. After treatment of lipoproteins (100 μg/ml) for 1 h, RAW264.7 cells were treated with 10 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor® 555–labeled pyrHSA together with or without 50 μg/ml of apoE3 for 1 h. The results shown are means ± S.D. (n = 3).
