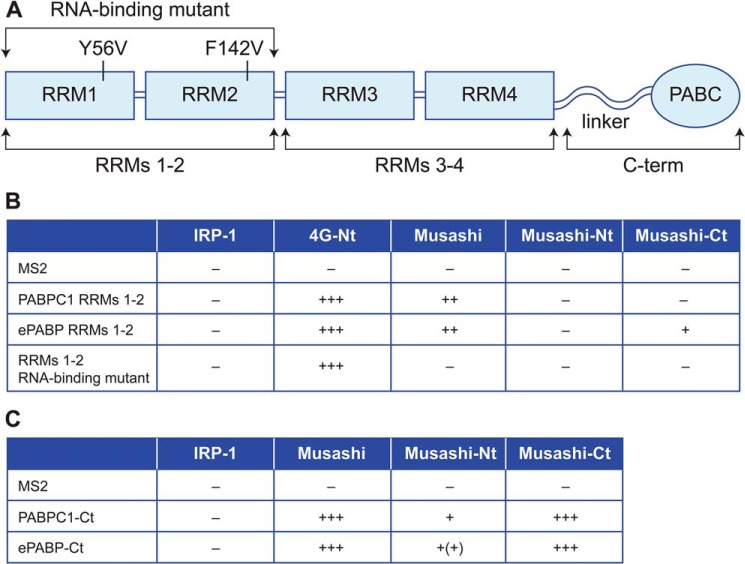
Figure 6.
Yeast two-hybrid analyses reveal a direct interaction between Musashi1 and the C terminus of ePABP and PABPC1. A, schematic representation of the structure of vertebrate PABPs and the specific constructs used for the interaction analyses. B, yeast two-hybrid analysis using transcription activator domain fusions with full-length Musashi, or Musashi N terminus (−Nt, amino acids 1–198), or C terminus (−Ct, amino acids 199–347) with DNA-binding domain fusions of X. laevis PABP1 and ePABP RRMs 1–2 or an RNA-binding defective version of PABPC1 RRMs 1–2. C, yeast two-hybrid analysis using DNA-binding domain fusions of PABP1 and ePABP C-terminal regions (−Ct) and the indicated Musashi transcription activator domain fusion constructs. IRP-1 and eIF4G N terminus (4G-Nt) represent negative and positive controls. The relative strength of tested interactions (assessed by colony growth and LexA-dependent β-gal expression) are represented by + symbols. The data in B and C are derived from three independent experiments.