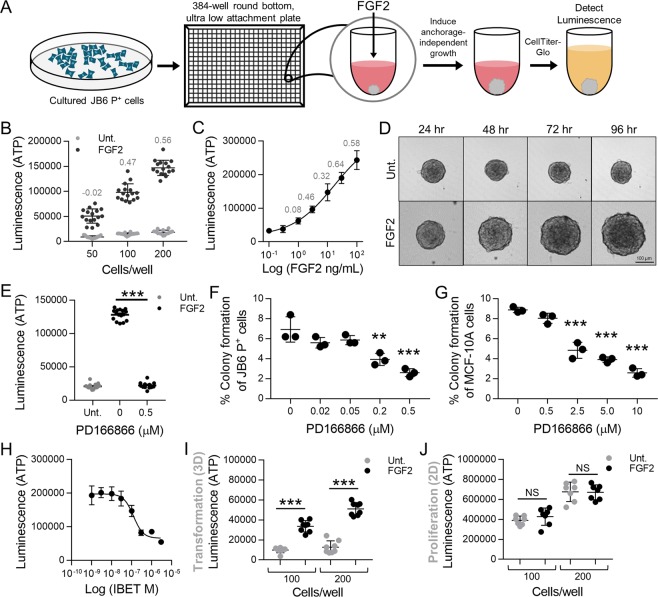
Figure 1.
Optimization and development of the transformation HTS. (A) Methodology schema of the transformation HTS. JB6 P+ cells were plated in 384-well round bottom ultra-low attachment conditions and stimulated with FGF2. JB6 P+ cell growth in ultra-low attachment conditions was measured with CellTiter-Glo that gives a luminescent signal stimulated by binding to ATP. ATP levels are proportional to the number of cells, and thus used as a measure of proliferation. (B) JB6 P+ cells were plated in 384-well round bottom, ultra-low attachment plates and treated with 30 ng/mL of FGF with either 50, 100, or 200 cells/well. 200 cells/well was the optimal cell density giving a Z-factor of 0.56. Fifty (50) and 100 cells/well gave Z-factors of −0.023 and 0.47 respectively. Each treatment group had 16 technical replicates. (C) A concentration response of FGF2 was performed with JB6 P+ cells at 200/cells per well. The EC50 was 15 ng/mL, however, 30 ng/mL gave the optimal Z-factor 0.644. Each treatment had 7 technical replicates. The concentration response stimulation was statistically analyzed using a nonlinear regression, dose-response with PRISM. (D) FGF2-stimulated transformation of JB6 P+ cells can be visually observed with JB6 P+ cells at 200 cells/well with or without FGF2 at 30 ng/mL over the 96-hour incubation. JB6 P+ cells congregate at the bottom of the round-bottom wells and untreated, do not grow, but with FGF2, do proliferate. (E) PD166866, a FGFR1 inhibitor, at 0.5 μM completely prevented FGF2-stimulated JB6 P+ cells growth in ultra-low attachment conditions. Untreated (Unt.) and FGF2 controls had 16 technical replicates and PD166866 had seven technical replicates. (F) PD166866 attenuates FGF2 (0.5 ng/mL)-stimulated JB6 P+ cell growth in soft agar. The soft agar assay was performed as described in Material/Methods. (G) PD166866 attenuates FGF2 (20 ng/mL)-stimulated MCF-10A cell growth in soft agar. The soft agar assay was performed as described in Material/Methods. Data are presented as mean ± S.D., statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001). (H) IBET concentration-dependently inhibits FGF2 stimulated growth in ultra-low attachment conditions. JB6 P+ cells were plated at 200 cells/well with FGF2 at 30 ng/mL. The IC50 of IBET inhibition is 0.12 µM. Each treatment had seven technical replicates. The concentration response inhibition was statistically analyzed using a nonlinear regression, dose-response with PRISM. (I) JB6 P+ cells were plated in 384-well round-bottom, low attachment plates (100 and 200 cells/well) and incubated at 37 °C for 48 hrs. FGF2 at 30 ng/mL significantly stimulates JB6 P+ cell growth in low attachment conditions compared to untreated controls (Unt.). Each treatment had seven technical replicates and data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (J) JB6 P+ cells were plated in 384-well flat-bottom, cell culture treated plates (100 and 200 cells/well) and incubated at 37 °C for 48 hrs. FGF2 at 30 ng/mL did not stimulate growth in 2D culture conditions compared to untreated controls (Unt.). Each treatment had seven technical replicates and data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001) NS, not significant.