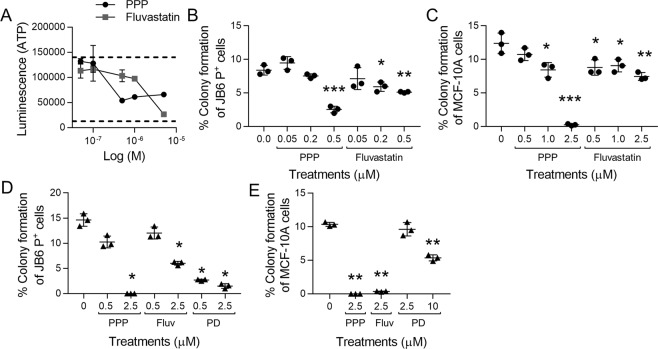
Figure 2.
PPP and fluvastatin significantly attenuate FGF2-stimulated transformation of epithelial cells. (A) PPP and fluvastatin concentration-dependently inhibit JB6 P+ cell growth in low attachment conditions. Dotted lines indicated FGF2 (top) and untreated controls (bottom). Each treatment had three technical replicates. JB6 P+ cells were cultured with the optimized parameters. (B) PPP and fluvastatin attenuate FGF2 (0.5 ng/mL)-stimulated JB6 P+ cell growth in soft agar at 0.5 µM and 0.2 and 0.5 µM respectively. The soft agar was performed as described in Materials/Methods with three technical replicates. (C) PPP and fluvastatin attenuates FGF2 (20 ng/mL)-stimulated MCF-10A cell growth in soft agar at 1.0 and 2.5 µM and 0.5, 1.0, and 2.5 µM respectively. The soft agar was performed as described in Materials/Methods with three technical replicates. (D) PPP and fluvastatin (Fluv) significantly attenuate MFTF (200 µg/mL)-stimulated JB6 P+ cell growth (1000 cells/well) in soft agar at 2.5 µM and PD166866 (PD) was significant at 0.5 and 2.5 µM. The soft agar was performed as described in Materials/Methods with three technical replicates. (E) PPP and fluvastatin (Fluv) significantly attenuate MFTF (200 µg/mL)-stimulated MCF-10A cell growth (1000 cells/well) in soft agar at 2.5 µM and PD166866 (PD) was significant at 10 µM. The soft agar was performed as described in Materials/Methods with three technical replicates. The soft agar assays were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).