Fig. 1.
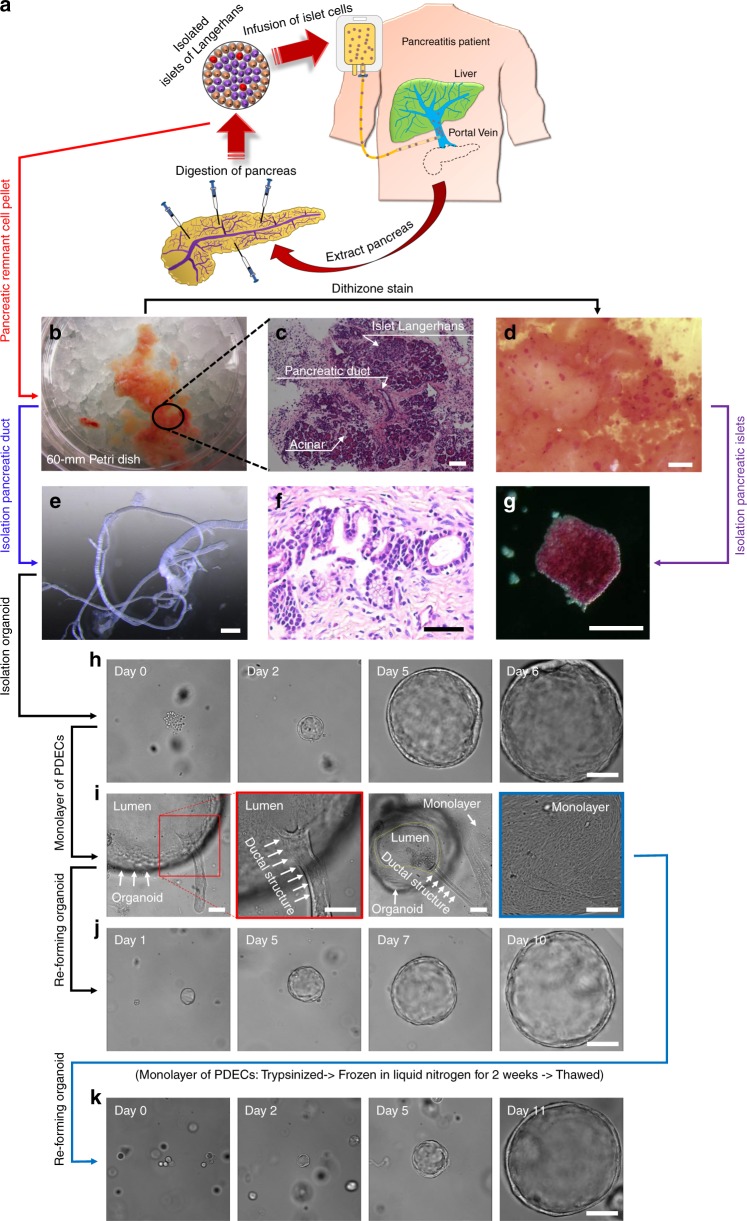
Isolation of patient-derived pancreatic ductal epithelium and islet cells. a Schematic representation of the total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation (TPIAT) procedure for pancreatitis patient. b Digested pancreatic remnant cell pellets were obtained following isolation of islet cells for infusion. c Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E stain) image demonstrates that the remnant cell pellet contains pancreatic islets, ductal epithelial cells, and acinar cells. d Pancreatic islets were identified by adding dithizone solution, where the color turned to red, and g isolated by manual pipetting. e Pancreatic ductal tissues were isolated by microdissection from the pancreatic remnant cell pellet following TPIAT. f H&E staining showed that pancreatic ductal epithelial cells were surrounded by collagen and connective tissue. h Pancreatic ductal epithelial cells (PDECs) were isolated from the ductal tissue and embedded in Matrigel matrix. PDECs grew into large spheres over time. i PDECs extend from the isolated organoid to form a monolayer on the surface of the substrate. j Ductal epithelial cell monolayers were re-formed into an organoid structure in the Matrigel and grew into a large sphere again. k Revived ductal epithelial cells following cryopreservation were embedded in the Matrigel and formed into large spheres over time. Scale bars: 50 µm (f), 100 µm (c, g–j and k), 500 µm (e), and 1000 µm (d)