Figure 5.
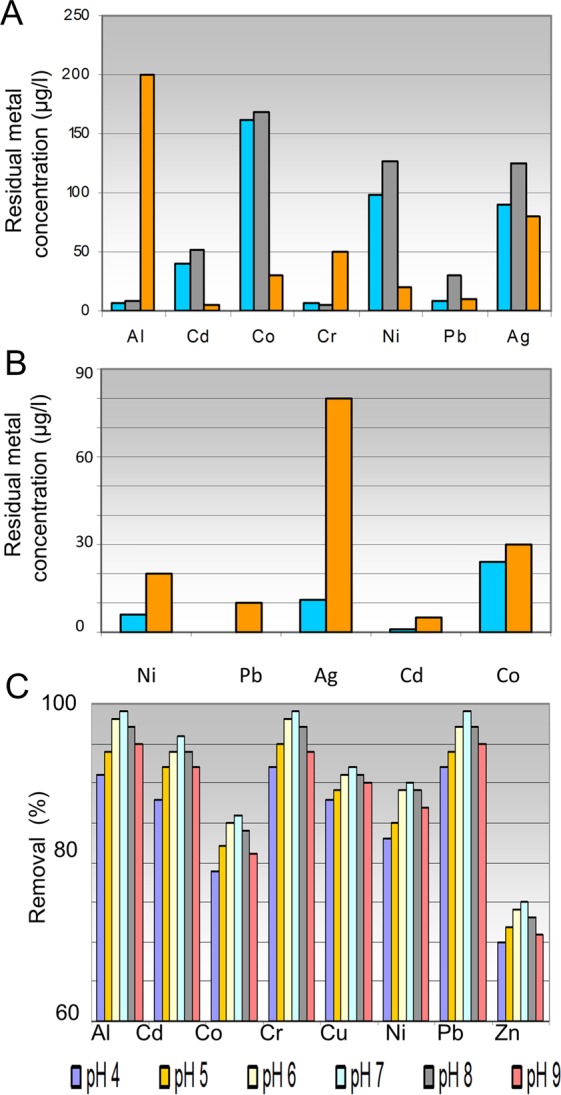
Demonstration of successive fractionation and remediation biotechnology for production of drinking water from multimetal contaminated water. Two-steps treatment of multimetal-contaminated water (1,000 µg/l per each metal in a metal mix) using dead insoluble cell walls (∼0.56 g fungal cell walls/L) is shown. (A) First step: Comparison of residual concentrations of ionic metals after 48 h treatment of contaminated water using insoluble cell walls from EH8, EH10 and EH11 (blue bar) or using fungal mixed grown microbiomes of EH8, EH10 and EH11 (grey bar) with the permitted concentrations (brown bar) for drinking water according to the German Drinking Water Ordinance. (B) Second step: Re-treatment of treated water from the first incubation using only dead insoluble cell wall mix led to reductions of concentrations of Ni, Ag, Cd and Co (blue bar) within 48 h even below the threshold values of the German Water Ordinance (brown bar) and (C) Removal (%) of metals (Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) using mixed insoluble cell walls from EH8, EH10 and EH11 depending on pH 4–9.
