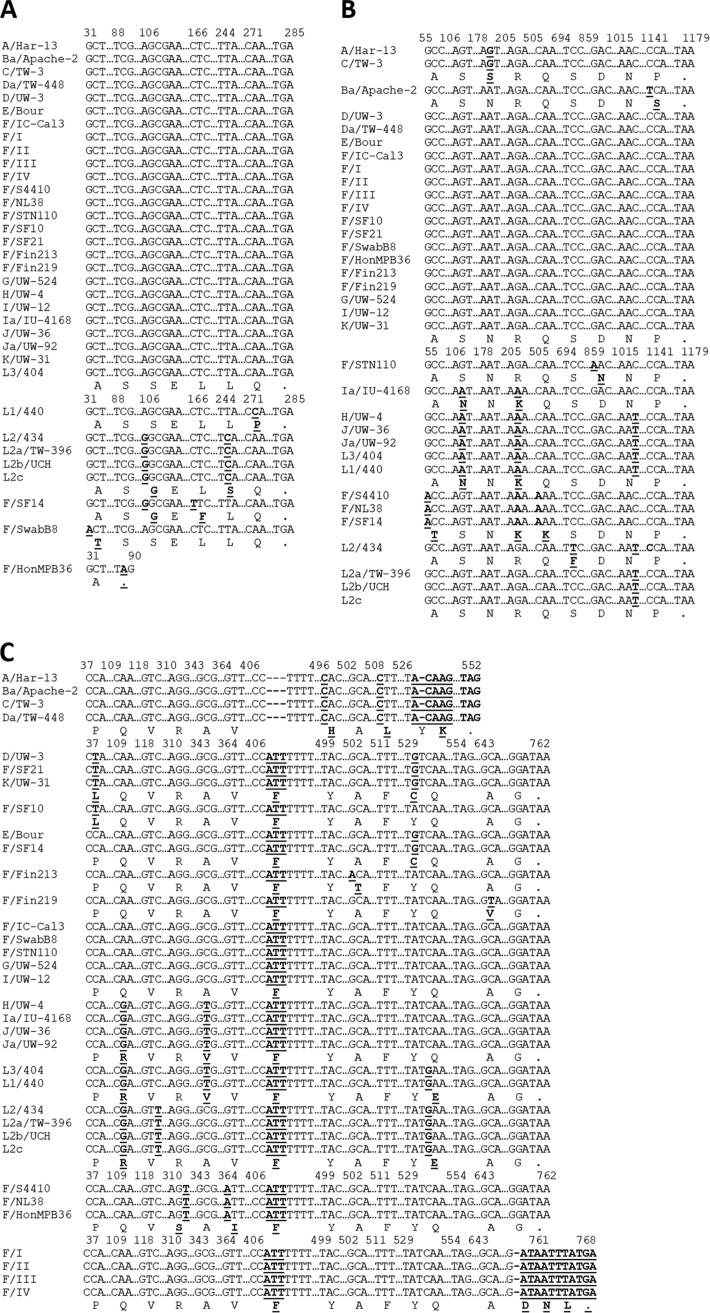
FIG 1.
C. trachomatis clinical strains F I to IV (F I-IV) contain a trpA frameshift causing TrpA elongation. (A to C) Partial nucleotide sequences showing trpR (A), trpB (B), and trpA (C) polymorphisms of the four serial clinical strains F I-IV compared to 20 C. trachomatis (Ct) reference strains (A/HAR13, Ba/Apache2, C/TW3, D/UW3, Da/TW448, E/Bour, F/ICCal3, G/UW57, H/UW4, I/UW12, Ia/IU4168, J/UW36, Ja/UW92, K/UW31, L1/440, L2/434, L2a/TW396, L2b/UCH-1/proctitis, L2c, and L3/404) including novel clinical F strains from the San Francisco Bay Area (n = 7) and all F strains previously sequenced and available from public databases (n = 59). A period in the sequence denotes homologous sequences that are not shown. Dashes denote nucleotide deletions at positions A408, T409, T410, and T528 for trpA of ocular strains and at position 758 for trpA of clinical strains F I-IV. Bold nucleotide letters denote substitution mutations, while bold amino acid letters denote nonsynonymous amino acid substitutions. Strains with homologous sequences are not shown: F/SotonF1-F4, F/Soton18-137, F/R4663-28312, F/STN15-22, F/UK35155-770010, F/SW4-5, F/SWFP, F/S1470-3948, F/NI1, F/NL30-36, F/Aus20, F/C55, F/It686-688, F/Sou9-100, F/Swab5, F/SwabB5, F/Fin106-219, and F/SF7-19. These strains had genes that were similar to the trpR gene of A/HAR13-L3/404, the trpB gene of D/UW-3-K/UW-31, and the trpA gene of F/IC-Cal3-I/UW-12.