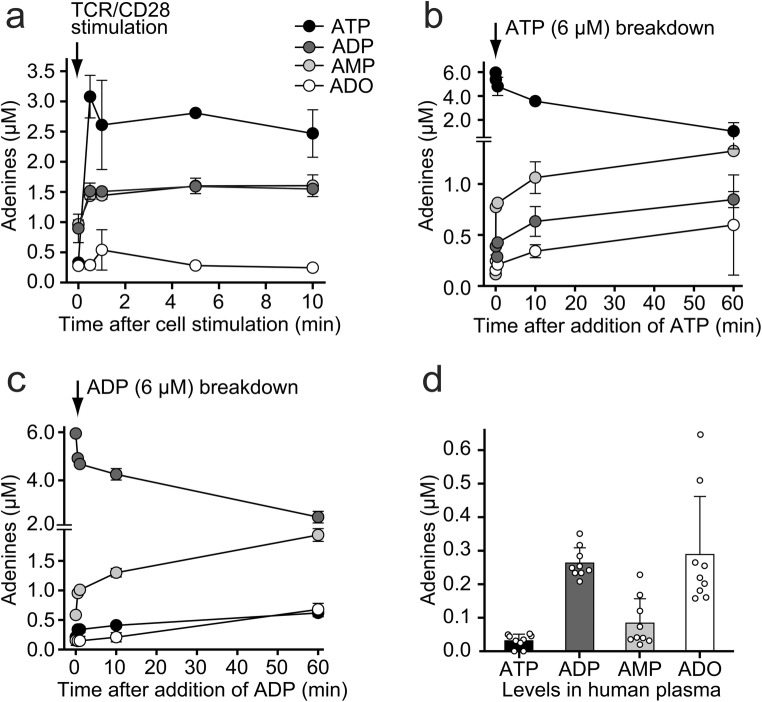
Fig. 1.
T cell stimulation triggers rapid ATP release and accumulation of extracellular ATP, ADP, and AMP. a ATP, ADP, and AMP accumulate in the extracellular space of stimulated T cells. Purified human CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-coated beads, and ATP, ADP, AMP, and adenosine (ADO) concentrations in the cell supernatants were measured with HPLC at the indicated times. b–c T cells are able to hydrolyze extracellular ATP and ADP. Exogenous ATP (b) or ADP (c) each at a final concentration of 6 μM was added to primary human CD4 T cells, and hydrolytic breakdown was monitored over time. Data shown (a–c) are means ± SD of n = 3 experiments with different cell preparations. d Human plasma from healthy subjects contains high levels of ADP. Plasma samples were collected from healthy human subjects, and the concentrations of ATP, ADP, AMP, and adenosine were determined with HPLC. Data shown are means ± SEM (n = 9)