FIGURE 6.
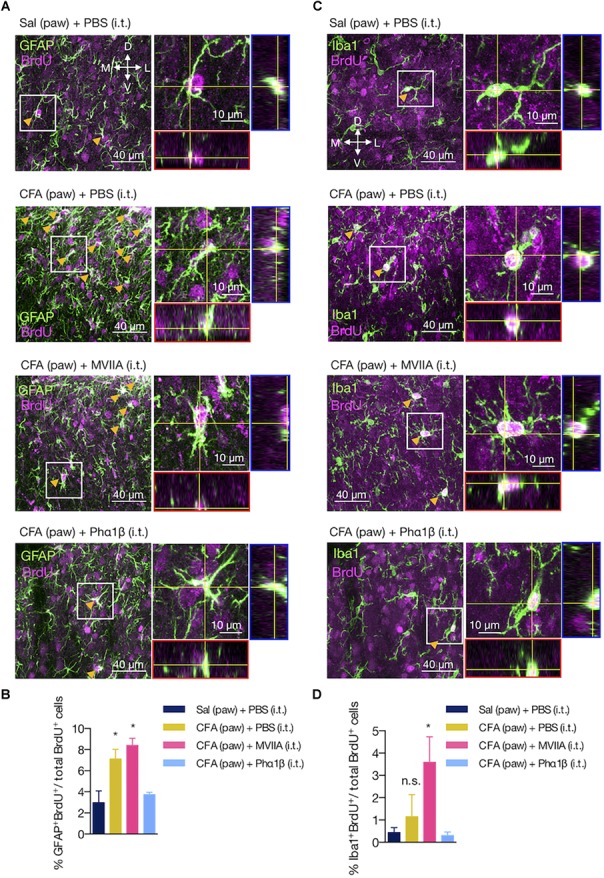
The Phα1β, but not the MVIIA toxin, reverses astrocyte proliferation induced by peripheral inflammation. (A,C) Representative images of (A) astrocyte and (C) microglia proliferation in the ipsilateral dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord. Arrows indicate examples of GFAP+BrdU+ or Iba1+BrdU+ cells. Insets contain the resulting confocal orthogonal view of the selected cells showing colocalization between GFAP or Iba1 with BrdU (in white). The lateral (blue) and bottom (red) rectangles represent the yz and xz views, respectively. (B,D) Quantification of (B) GFAP+BrdU+ or (D) Iba1+BrdU+ cells relative to the total number of BrdU+ cells (n = 3/group, three slices per animal). Scale bars are 40 or 10 μm for the low and high magnification images, respectively. M: medial; L: lateral; D: dorsal; V: ventral (coordinates relative to the central canal). Summary data are represented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; n.s., not significant [compared to the Sal (paw) + PBS (i.t) group].
