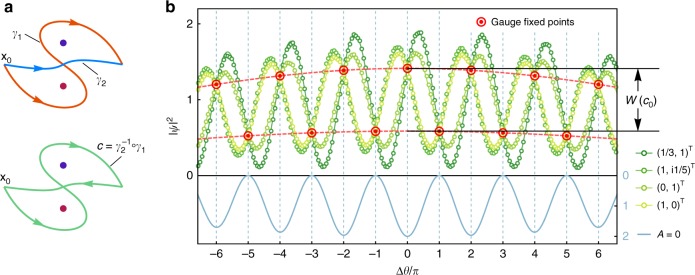
Fig. 4.
Extracting Wilson loops from gauge fixed points. a For two arbitrary beams γ1, γ2 interfering on the screen, the Wilson loop of the concatenate path can be extracted from the interference fringes of the two beams. b Four intensity interference curves corresponding to four different incident spinors , , , for the non-Abelian AB system shown in Fig. 3a with vortex fluxes , , where circles and solid curves represent numerical and analytical results, respectively. Their intersections, marked by red targets, are the gauge fixed points, which are located at the crests and troughs of the interference fringes (light blue curve) of . The maximal difference between the envelops of even and odd gauge fixed points gives the Wilson loop of