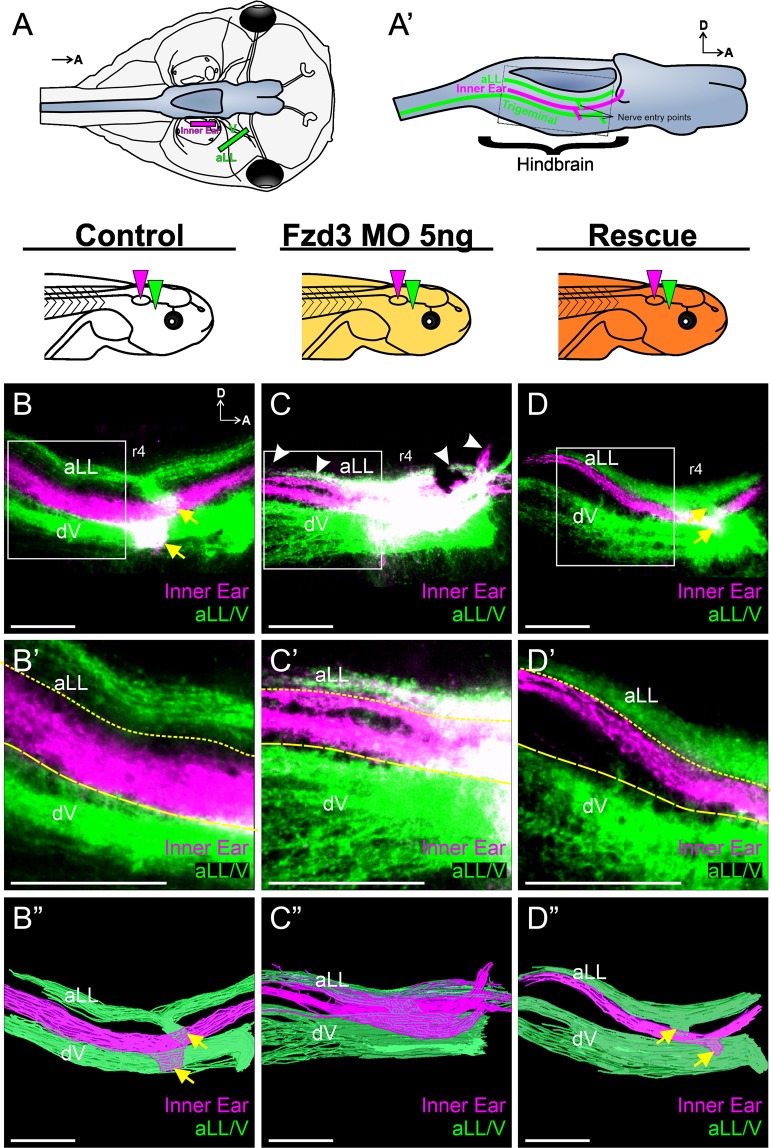
Figure 1.
Xenopus vestibular afferents display aberrant central projections following Fzd3 knockdown. (A) Schematic showing a dorsal view of a stage 46 Xenopus laevis tadpole and location of lipophilic dye placement. Lipophilic dyes were implanted into the ear (magenta) and into the anterior lateral line (aLL) and trigeminal (V) nerves (green). Brain is colored blue. (A’) Schematic showing a side view of a brain highlighting the location of the central projections from anterior lateral line (aLL), inner ear, and trigeminal afferents that would be labeled from the dye placement in (A) Dotted box represents the approximate area imaged. Confocal images of hindbrains from control animals (n = 6) (B), of animals injected with 5 ng Fzd3 morpholino (n = 12) (C), and of rescue animals injected with 5 ng Fzd3 morpholino plus 500 pg mouse Fzd3 mRNA (n = 9) (D). White arrowheads indicate aberrant projections. Yellow arrows indicate nerve entry points. (B’–D’) Higher magnification of boxed areas in (B–D). Short-dash and long-dash yellow lines represent the approximate ventral boundary of the anterior lateral line afferent projections and dorsal boundary of the trigeminal afferent projections, respectively. (B”–D”) Three-dimensional reconstructions of entire confocal stacks shown in (B–D). r4, rhombomere 4; dV, descending trigeminal tract; D, dorsal; A, anterior. Orientation for panels (B–D”) as in (B) Diagrams represent treatment (white, control; gold, Fzd3 morpholino; orange, Fzd3 morpholino plus Fzd3 mRNA) and colored wedges represent lipophilic dye placement (magenta, inner ear; green, lateral line and trigeminal nerves). Scale bars represent 100 µm.