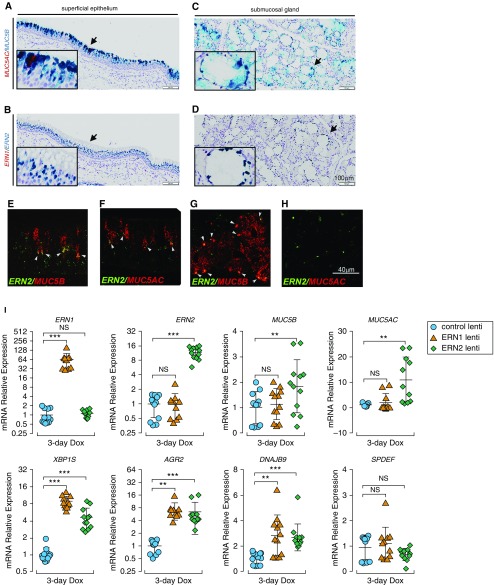
Figure 1.
ERN2 is expressed with MUC5B and MUC5AC in mucin-secreting cells in vivo and promotes MUC5B and MUC5AC expression in human airway epithelium in vitro. (A–H) Expression of ERN2, MUC5B, and MUC5AC mRNA was detected using RNAscope assays in pseudostratified superficial epithelium (A, B, E, and F) and submucosal glands (C, D, G, and H) of proximal cartilaginous airways of normal adult human lung. Expression of MUC5AC with MUC5B (A and C) and ERN1 with ERN2 (B and D) was detected by RNAscope duplex chromogenic assays. Insets show high-power view of arrow-pointed areas. Expression of ERN2 with MUC5B (E and G) and ERN2 with MUC5AC (F and H) mRNAs was detected by RNAscope multiplex dual-fluorescent assays in human cartilaginous airway epithelia. Coexpression of red and green signals in the same cell is highlighted by white arrowheads (E–G). Micrographs in A–H are representative of n = 3 lung tissue from donors without preexisting pulmonary diseases. Scale bars: A–D, 100 μm; E–H, 40 μm. (I) Doxycycline (Dox)-induced expression of ERN1 or ERN2 in primary human airway epithelia. Lentiviral stably infected human airway epithelial cells were cultured under acute lung injury conditions for 5 days before 3-day Dox administration (250 ng/ml) in the basolateral acute lung injury media. mRNA expression of ERN1 and ERN2; mucin-related genes MUC5B, MUC5AC, AGR2, and SPDEF; and unfolded protein response genes XBP1S and DNAJB9 was determined by SYBR-Green quantitative (q) RT-PCR or Taqman assays. Graphs represent means ± SD of n = 3–4 human airway epithelial cultures obtained from three non–cystic fibrosis/nonsmoker donors, and data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared with control subjects. NS = not significant.