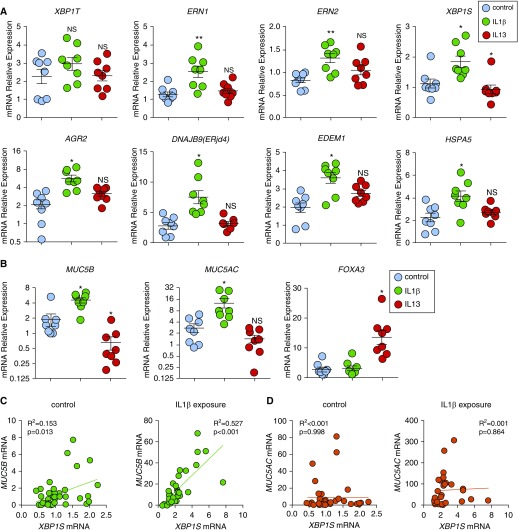
Figure 2.
IL-1β induces unfolded protein response and XBP1S that is associated with MUC5B expression in human airway epithelial (HAE) cells. (A) Unfolded protein response genes were acutely induced after IL-1β exposure. HAE cells were cultured under acute lung injury conditions for 4 weeks to allow full differentiation before exposure with IL-1β and IL-13. Both IL-1β and IL-13 were added in basolateral acute lung injury media at 10 ng/ml for 24 hours. Expression of unfolded protein response genes XBP1T (total XBP1), ERN1, ERN2, XBP1S, AGR2, DNAJB9, EDEM1, and HSPA5 was quantified by SYBR-green qRT-PCR or Taqman assays. (B) Expression of mucin genes MUC5B and MUC5AC and goblet cell transcription factor FOXA3 was quantified by Taqman assay. Data are presented as mean ± SE of n = 1 culture of HAE cells from eight non–cystic fibrosis, nonsmoker donors, analyzed with paired one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with control subjects. HAE cells treated with IL-1β are labeled with green, IL-13 are labeled with red, and control subjects are labeled with blue. (C and D) mRNA expression of XBP1S versus MUC5B (C) and XBP1S versus MUC5AC (D) in HAE cells that were treated basolaterally with or without IL-1β 10 ng/ml (IL-1β exposure or control) for 5 days was analyzed by linear regression. The R2 and P values were compared. Normal HAE cells obtained from n = 40 non–cystic fibrosis donor lungs and n = 33 non–cystic fibrosis donor lungs were tested for control and IL-1β exposure, respectively. NS = not significant.