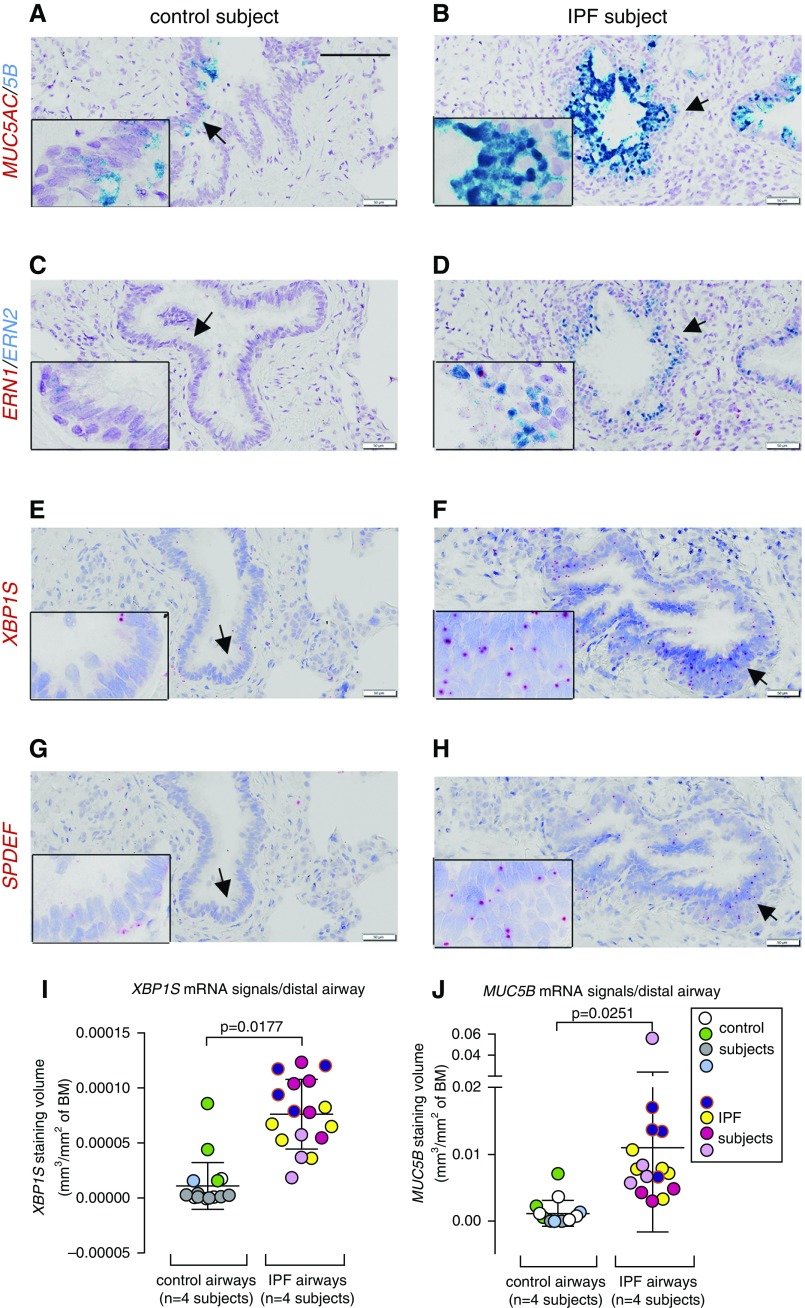
Figure 5.
Expression of MUC5AC/MUC5B, ERN1/ERN2, XBP1S, and SPDEF mRNAs in the distal airways of human subjects without idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and with IPF. (A–H) mRNA expression of MUC5AC/MUC5B (A and B) and ERN1/ERN2 (C and D) was detected by RNAscope Duplex assays, and XBP1S (E and F) and SPDEF (G and H) mRNAs were detected by BaseScope assays in distal airways (<0.5 mm) of control subjects (n = 4) and patients with IPF (n = 8). Scale bar, 100 μm. Insets show higher power views of arrow-pointed areas. (I and J) Quantification of XBP1S (I) and MUC5B (J) mRNA signals in the distal human airways (including all the airways with luminal diameter <500 μm) (i.e., terminal airways, regardless of staining status) was determined by morphometric analysis of staining volume density detected by Basescope and RNAscope, respectively (n = 4 of control subjects and n = 4 of IPF subjects). Analysis for XBP1S mRNA signal quantification was performed with n = 4.5 ± 1.9 and n = 4.3 ± 1 distal airways/subject, mean ± SD, for control and IPF, respectively. For MUC5B mRNA signal quantification, analysis was performed with n = 3.75 ± 1.3 and n = 4 ± 0.8 distal airways/subject, means ± SD, for control and IPF, respectively. Each colored dot represents measurement of one airway, and each color indicates measurements obtained from the same subject. Data represent mean ± SD of signal volume density/distal airway in either group, and the differences of means between the two groups (denoted by P values) were analyzed by linear mixed-effects model with subject identification number as random intercept variable. BM = basement membrane.