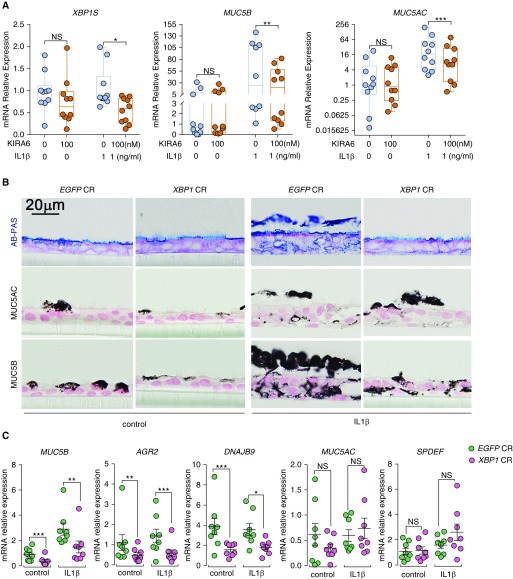
Figure 7.
KIRA6 and XBP1 CRISPR inhibit IL-1β–induced MUC5B expression in primary human airway epithelial (HAE) cells. (A) KIRA6 partially inhibits XBP1S, MUC5B, and MUC5AC. Primary HAE cells were cultured under acute lung injury (ALI) condition for 4 weeks to allow full differentiation before IL-1β exposure. At 24 hours after IL-1β (1 ng/ml in basolateral ALI media) exposure, KIRA6 was added in ALI media of the HAE cells preexposed with IL-1β at the final concentration of 100 nM. Expression of XBP1S, MUC5B, and MUC5AC mRNAs was determined 72 hours after KIRA6 treatment by SYBR green qRT-PCR or Taqman assays. Data represent n = 1 HAE cell culture from 10 independent non–cystic fibrosis/nonsmoker donors. Data were analyzed with two-tailed, ratio paired Student’s t test. (B) XBP1 CRISPR inhibited MUC5B expression. Primary HAE cells were stably infected with lentiviruses expressing control CRISPR (EGFP CR) or XBP1 CRISPR (XBP1 CR) and cultured under ALI for 4 weeks to allow full differentiation before IL-1β exposure (1 ng/ml). Five days after exposure with and without IL-1β, HAE cells were collected for histologic analysis, including alcian blue/periodic acid–Schiff (AB-PAS), MUC5AC, and MUC5B immunohistochemical staining. Micrographs are representatives of lenti-CRISPR-infected HAE cells obtained from three non–cystic fibrosis, nonsmoker donors. (C) Expression of MUC5B, AGR2, DNAJB9, MUC5AC, and SPDEF mRNAs in XBP1 CRISPR-targeted cells was analyzed with Taqman assays. Graphs represent mean ± SE with n = 1 HAE cell culture from eight different non–cystic fibrosis, nonsmoker donors. Data were analyzed with two-tailed, paired Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. NS = not significant.