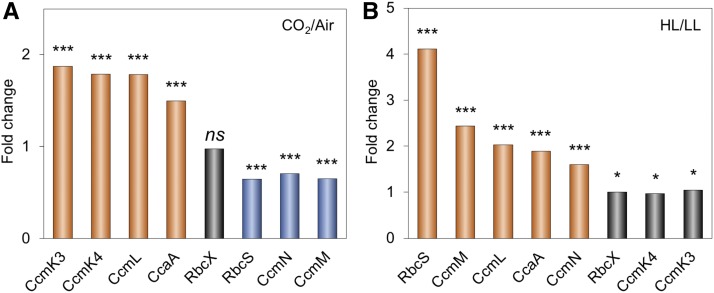
Figure 3.
Changes in Carboxysome Protein Stoichiometry upon Increases in CO2 Levels and Light Intensity.
(A) Comparison of carboxysome protein stoichiometry under CO2 treatment. Increase in the CO2 concentration resulted in the rise of CcmK3, CcmK4, CcaA, and CcmL contents and the decline of RbcS, CcmN, and CcmM contents.
(B) Comparison of carboxysome protein stoichiometry under light intensity treatment. Increased light intensity led to the elevation of RbcS, CcmM, CcmL, CcaA, and CcmN contents, whereas the abundance of RbcX, CcmK3, and CcmK4 contents per carboxysome did not change dramatically.
Mann-Whitney U-tests were performed to compare the numbers of functional units of individual carboxysome proteins changed from CO2/ML to Air/ML (A) and from HL to LL (B). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.005; ns, P > 0.05.