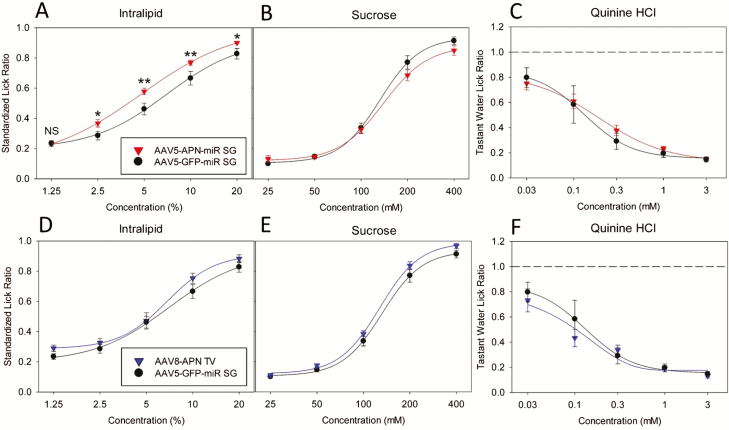
Figure 8.
Brief-access lick response testing of APN KO mice with supplemented salivary or systemic adiponectin relative to untreated APN KO littermates. Brief-access lick response testing results of APN KO mice with supplemented salivary adiponectin (AAV5-APN-miR SG, red) compared with untreated APN KO (AAV5-GFP-miR SG, black) mice are shown in panels A, B, and C. Of the tastants tested, mice with supplemented salivary APN had a significantly increased (F1,22 = 8.247; P = 0.009) response to Intralipid (A) relative to APN KO mice, as determined by two-way repeat-measure ANOVA (α = 0.05). In the case of a significant ANOVA, a post hoc Holm–Sidak t-test (α = 0.05) was applied to compare the significance of the lick response for each tastant concentration (NSP > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, **P < 0.01). Mice with supplemented salivary adiponectin (A, red) had a significantly increased lick response relative to APN KO mice (A, black) at each concentration of Intralipid except the lowest (1.25% Intralipid, P > 0.05). Salivary adiponectin supplementation mice did not display significantly altered lick behavior from APN KO mice for sucrose (F1,22 = 0.872; P = 0.361; B) or QHCL (F1,22 = 0.134; P=0.718; C). APN KO mice with systemically supplemented adiponectin (AAV8-APN TV, blue) did not display a significant difference in lick behavior from APN KO mice (black) for Intralipid (F1,15 = 1.722; P = 0.209; D), sucrose (F1,15 = 3.452; P=0.083; E), or QHCL (F1,16 = 0.295; P = 0.595; F).